The Link Between Food Safety and Compliance in Manufacturing
What Is Food Safety and Compliance in Manufacturing, and Why Is It Important?
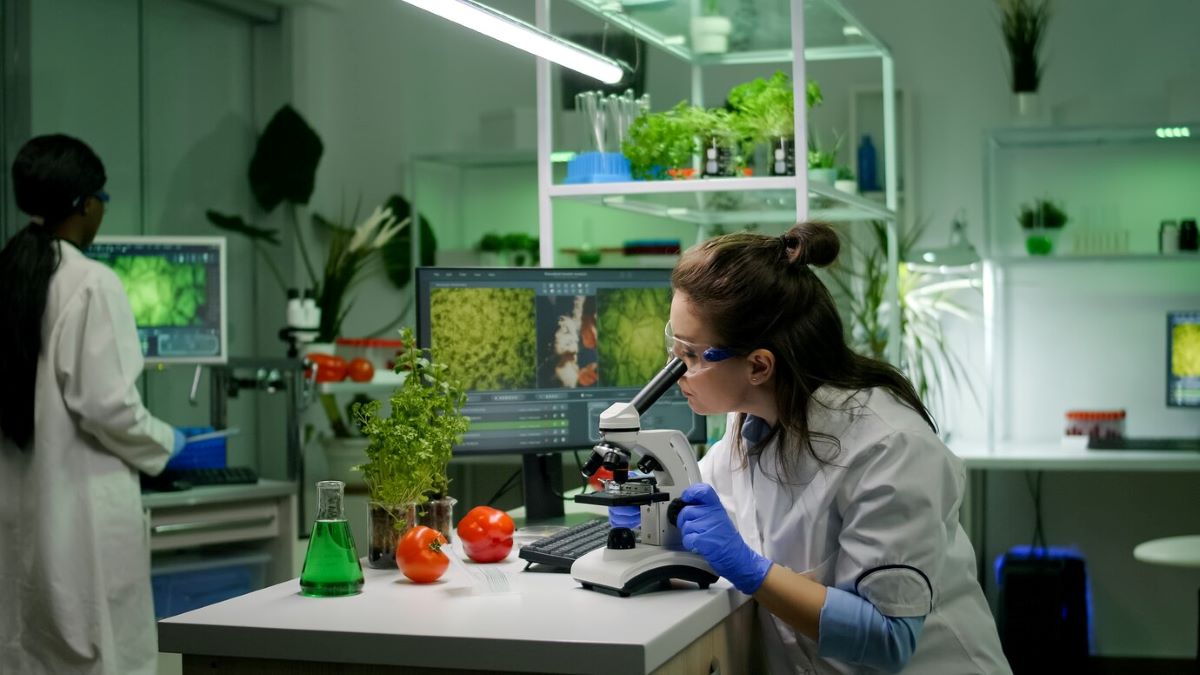
Food safety in manufacturing refers to the practices and protocols that prevent contamination, spoilage, and health hazards throughout the production process. Compliance in manufacturing means adhering to established regulations, standards, and legal requirements set by governing bodies to ensure these safety measures are consistently implemented.
The link between food safety and compliance in manufacturing creates a framework where regulatory oversight drives operational excellence. Without compliance structures, food safety becomes subjective and inconsistent. Regulations transform best practices into mandatory requirements, establishing baseline standards that all manufacturers must meet.
This relationship protects public health while creating accountability across the supply chain. When manufacturers follow food manufacturing regulations like those outlined in wholesale food safety guidelines, they implement systematic controls at every production stage—from raw material sourcing to final product distribution. These controls include temperature monitoring, sanitation protocols, allergen management, and contamination prevention measures.
Compliance supports safe food production through several mechanisms:
- Standardization of hygiene practices across facilities
- Verification systems that confirm safety measures are working
- Traceability protocols that track products through the supply chain
- Documentation requirements that create accountability
- Regular audits that identify gaps before problems occur
The regulatory framework also levels the competitive playing field. All manufacturers operate under the same food safety expectations, preventing shortcuts that could compromise consumer health. This standardization builds consumer confidence in the food supply, knowing that products meet verified safety criteria regardless of which facility produced them.
For manufacturers, compliance isn’t merely about avoiding penalties. It represents a systematic approach to risk management that protects both consumers and business operations. A single food safety failure can result in recalls, legal action, and irreparable brand damage—consequences far exceeding the investment required for proper compliance programs.
What Are the Key Food Safety Regulations Affecting Manufacturers?
Food safety regulations create a universal framework that every manufacturer must follow, regardless of product type or production scale. These regulations establish minimum standards for hygiene, contamination prevention, and traceability across all stages of food production. The SQF Code stands as one of the most comprehensive certification programs, providing detailed requirements for everything from raw material handling to finished product distribution.
Which Regulatory Agencies Oversee Food Manufacturing?
Multiple regulatory agencies share responsibility for enforcing food safety standards, each with distinct jurisdictions and specializations. In Queensland, Australia, Queensland Health monitors food safety compliance across restaurants, retail outlets, and general food businesses. Safe Food Production Queensland takes a more targeted approach, managing industry-specific safety schemes for high-risk sectors including meat processing, dairy production, egg farming, seafood handling, and horticultural operations.
These regulatory agencies conduct regular inspections, investigate foodborne illness outbreaks, and have authority to issue penalties or suspend operations when violations occur. Manufacturers dealing with multiple product categories may need to satisfy requirements from several agencies simultaneously.
What Role Do Local Councils Play in Food Safety Compliance?
Local councils serve as the frontline regulatory authority for most food manufacturers, issuing essential licenses and permits required before operations can begin. Every food business must register with their local council and obtain approval for their premises, equipment, and operational procedures. Council health inspectors perform routine assessments to verify ongoing compliance with hygiene standards, waste management protocols, and structural requirements.
The licensing process through local councils includes:
- Initial premises inspection to assess suitability for food production
- Equipment verification to ensure proper installation and maintenance
- Food safety program approval demonstrating systematic hazard control
- Annual renewal requirements with updated documentation
Manufacturers cannot legally operate without valid council approval, making this relationship critical to business continuity.
How Are Genetically Modified Foods Regulated?
Genetically modified (GM) foods face additional regulatory scrutiny through specialized standards that require pre-market evaluation and approval. Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ) assesses all GM foods before they can be sold, examining potential health risks, allergenicity, and nutritional composition. Manufacturers using GM ingredients must maintain detailed records demonstrating compliance with approved varieties an
How Does Compliance Ensure Food Safety Throughout Manufacturing Stages?
Compliance frameworks create structured checkpoints at every phase of production, preventing hazards from entering the food supply chain. Each manufacturing stage—from raw material receipt through processing, packaging, distribution, and final sale—presents unique contamination risks that regulatory standards specifically address through mandatory controls and verification procedures.
Critical Food Safety Stages in Production
1. Processing
This is the first step where raw ingredients are transformed. During this stage, biological, chemical, and physical hazards pose the greatest threats. To ensure safety, compliance protocols require:
- Monitoring temperatures during cooking or pasteurization
- Validating kill steps for harmful microorganisms
- Documenting procedures for handling ingredients
For example, a meat processing facility must maintain specific time-temperature combinations to eliminate E. coli and Salmonella. Continuous recording devices are used to provide evidence of compliance.
2. Manufacturing
This stage involves assembling, formulating, and preparing finished products. Here, compliance mandates strict allergen control programs to prevent cross-contact between production lines. It also emphasizes the importance of validating equipment cleaning processes—manufacturers must prove that sanitation procedures effectively remove allergens and pathogens between product runs. To minimize contamination risks, production scheduling often separates items containing allergens from those that are allergen-free.
3. Distribution
During transport and storage, temperature control challenges and opportunities for physical contamination arise. Compliance requires documentation of the cold chain for refrigerated items, records of vehicle sanitation practices, and implementation of pest control programs at warehouses. Real-time monitoring using GPS-enabled temperature loggers creates audit trails that demonstrate continuous compliance from the factory to the retail location.
4. Sale
The final transfer of custody occurs at this stage, where it is crucial to maintain the integrity of the product. Retailers receiving manufactured goods verify compliance by reviewing certificates of analysis, tracing batch codes, and validating shelf-life claims. Point-of-sale compliance includes ensuring proper storage conditions and training staff on disclosing allergen information.
Contamination Prevention Through Compliance Measures
Compliance helps reduce contamination risks through prerequisite programs that establish basic sanitary conditions. These foundational controls include:
- Supplier approval systems that verify ingredient safety before materials enter facilities
- Receiving inspections checking for signs of pests, package integrity issues, and temperature abuse
- Zoning protocols separating areas where raw food and ready-to-eat food are handled to prevent cross-contamination
- Personnel practices requiring handwashing stations and protective clothing for workers
Why Is Adherence to Food Safety Codes Like SQF Essential for Manufacturers?
The SQF Code provides manufacturers with a comprehensive framework that addresses critical safety elements from raw material handling to finished product distribution. This internationally recognized certification system establishes rigorous standards for hygiene practices, allergen control, and environmental monitoring that go beyond basic regulatory requirements. Manufacturers implementing SQF protocols gain access to global markets while demonstrating their commitment to producing safe, high-quality food products.
What Specific Guidelines Does the SQF Code Provide?
The SQF Code outlines detailed requirements for maintaining sanitary conditions across all production areas. These guidelines specify cleaning frequencies, sanitizer concentrations, and verification procedures for equipment and surfaces that contact food. Temperature controls, cross-contamination prevention measures, and personnel hygiene protocols form the foundation of these standards.
Allergen management represents a critical component of SQF compliance. The code requires manufacturers to:
- Identify and document all allergens present in the facility
- Implement physical separation or validated cleaning procedures between allergen-containing products
- Establish clear labeling protocols that accurately communicate allergen information
- Train staff on allergen handling procedures and cross-contact prevention
- Conduct regular testing to verify the effectiveness of allergen controls
How Does SQF Build a Food Safety Culture?
A food safety culture emerges when organizations integrate safety principles into every decision and action. SQF certification requires leadership commitment, employee engagement, and continuous improvement practices that transform safety from a compliance checkbox into a core operational value. Management must demonstrate active participation in safety initiatives, allocate resources for training programs, and establish open communication channels where workers feel empowered to report concerns.
The code mandates regular training sessions that keep food safety awareness at the forefront of daily operations. Employees learn to recognize potential hazards, understand their role in preventing contamination, and take ownership of safety outcomes. This cultural shift reduces human error incidents and creates teams that proactively identify improvement opportunities rather than simply following procedures.
What Role Does SQF Play in Managing Compliance Risks?
Compliance risks in food manufacturing extend beyond immediate safety concerns to include legal liability, market access restrictions, and reputational damage. The SQF Code’s systematic approach helps manufacturers identify vulnerabilities before they escalate into serious incidents
What Are the Legal and Certification Requirements for Food Manufacturing Compliance?
Food manufacturers cannot legally operate without securing the appropriate permits and licenses from regulatory authorities. Local councils typically issue business licenses that authorize food production activities, while health departments grant specific permits verifying that facilities meet sanitation and safety standards. These approvals demonstrate that manufacturing sites comply with zoning regulations, building codes, and operational requirements before any food production begins.
The legal requirements food manufacturing businesses must satisfy vary based on product type and intended market. Standard requirements include:
- Business registration and food handling licenses
- Health department inspections and facility approvals
- Water quality certifications for production use
- Waste disposal permits for manufacturing byproducts
- Import/export licenses for international trade
Certification standards organic products demand additional verification processes beyond basic licensing. Organic certification requires manufacturers to document their entire supply chain, proving that ingredients originate from certified organic sources and that production methods avoid synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or genetic modification. Accredited certification bodies conduct regular audits to verify compliance with organic standards, examining everything from ingredient sourcing to cleaning procedures that prevent cross-contamination with non-organic materials.
Biodynamic certification represents an even more rigorous standard, requiring adherence to holistic farming principles and specific production timing aligned with natural cycles. Manufacturers pursuing these premium certifications must maintain detailed records, implement strict segregation protocols, and undergo annual inspections to retain their certified status.
The legal implications of non-compliance with food safety laws extend far beyond monetary penalties. Manufacturers operating without proper licenses face immediate shutdown orders and potential criminal prosecution. Violations resulting in contaminated products can trigger product recalls costing millions in direct expenses, lost revenue, and destroyed inventory. Serious safety breaches that harm consumers may result in:
- Civil lawsuits seeking compensation for injuries or illnesses
- Criminal charges against company executives for negligence
- Permanent revocation of operating licenses
- Mandatory facility closures until corrective actions are completed
- Public disclosure of violations damaging brand reputation
Regulatory agencies maintain public databases listing non-compliant manufacturers, creating lasting reputational damage that affects customer relationships and market access. Insurance companies may deny coverage or dramatically increase premiums for businesses with compliance violations, while retailers and distributors often terminate contracts with non-compliant suppliers to protect their own liability

How Does Compliance Protect Consumer Health and Product Integrity?
Regulatory compliance creates a protective barrier between potential hazards and the final consumer by establishing systematic controls at every point in the manufacturing process. Consumer health protection begins when manufacturers implement documented procedures for ingredient verification, temperature controls, and sanitation protocols that prevent biological, chemical, and physical contaminants from entering products.
Maintaining Quality Throughout the Supply Chain
Compliance frameworks require manufacturers to establish traceability systems that track ingredients from suppliers through production to distribution. These systems enable rapid identification of quality issues before products reach consumers. When a manufacturer follows regulatory standards, each batch undergoes documented testing and verification, creating multiple checkpoints where substandard products can be identified and removed.
Temperature monitoring requirements exemplify how compliance maintains quality. Refrigerated products must remain within specific temperature ranges during storage and transport. Compliance mandates continuous monitoring and documentation, preventing bacterial growth that could compromise both safety and product characteristics like texture, flavor, and nutritional value.
Preventing Contamination at Critical Points
Contamination prevention operates through layered defense mechanisms built into compliance requirements. Physical barriers separate raw materials from finished products, preventing cross-contamination. Staff hygiene protocols, including handwashing stations and protective clothing requirements, eliminate human-related contamination risks.
Allergen management protocols demonstrate how compliance prevents specific contamination threats. Manufacturers must:
- Maintain separate production lines or implement thorough cleaning between allergen-containing products
- Label equipment and storage areas clearly
- Train staff on allergen handling procedures
- Verify cleaning effectiveness through testing
Environmental monitoring programs required by compliance standards detect potential contamination sources before they affect products. Regular testing of surfaces, air quality, and water systems identifies microbial risks, allowing corrective action before contamination occurs.
Building Consumer Trust Through Standards Adherence
Product integrity assurance through compliance creates measurable benefits for brand reputation and market position. When manufacturers consistently meet regulatory standards, consumers develop confidence that products will deliver expected safety and quality every time they purchase.
Third-party certifications like SQF provide visible proof of compliance commitment. These certifications require regular audits by independent assessors, giving consumers assurance beyond manufacturer claims. Retailers increasingly require such certifications, recognizing that compliance reduces their own liability risks and protects their reputation.
Documented compliance history
Conclusion
Why must manufacturers treat food safety and compliance as inseparable priorities? The link between food safety and compliance forms the foundation of successful food manufacturing operations, where regulatory adherence directly translates to consumer protection and business sustainability.
Manufacturers who integrate both elements create systems that protect public health while building competitive advantages. Compliance frameworks provide the structure needed to implement consistent safety practices across all production stages.
The business case for prioritizing both includes:
- Risk mitigation – Preventing costly recalls, legal actions, and operational shutdowns. This is similar to the sustainability risk mitigation strategies employed in real estate investing.
- Market access – Meeting requirements for domestic and international trade
- Operational efficiency – Standardized processes that reduce waste and improve productivity, akin to the principles of operational efficiency.
- Workforce safety – Creating environments where employees understand and follow safety protocols
The Link Between Food Safety and Compliance in Manufacturing extends beyond regulatory checkboxes. It represents a commitment to excellence that distinguishes industry leaders from those who view compliance as a burden rather than an opportunity.
Manufacturers investing in robust food safety programs supported by comprehensive compliance strategies position themselves for long-term success. These organizations recognize that consumer trust, once earned through consistent safety performance, becomes their most valuable asset.
The path forward requires manufacturers to view food safety and compliance as integrated business functions rather than separate departments. This holistic approach ensures that every decision, from ingredient sourcing to final distribution, reflects a commitment to producing safe, high-quality food products that meet both regulatory standards and consumer expectations.
Click here for more Implementing a Robust Food Safety Compliance System for Audits
Implementing a Robust Food Safety Compliance System for Audits
Why Should Businesses Implement a Robust Food Safety Compliance System for Audits?
A strong food safety compliance system protects consumers from foodborne illnesses and businesses from expensive recalls, legal issues, and damage to their reputation. By implementing a comprehensive system, businesses can create a structured framework that identifies potential hazards, establishes controls, and maintains consistent safety standards across all operations.
The Consequences of Inadequate Food Safety Measures
The consequences of insufficient food safety measures go beyond immediate health risks. Businesses may face:
- Financial losses from product recalls, which can cost millions in direct expenses and lost revenue
- Legal penalties including fines, sanctions, and potential criminal charges for serious violations
- Brand reputation damage that can take years to rebuild after a food safety incident
- Loss of market access when failing to meet retailer or export requirements
The Importance of Food Safety Audits
Food safety audits are a critical component of an effective Food Safety Compliance System, verifying whether processes and procedures are functioning as intended. These systematic examinations assess compliance with regulatory requirements, industry standards, and internal protocols. By integrating audits within a Food Safety Compliance System, businesses can identify gaps before they escalate into serious incidents, gaining actionable insights for continuous improvement.
Regular audit cycles create accountability throughout the organization. Internal audits conducted monthly or quarterly catch issues early on, while external audits by third-party certifiers or regulatory bodies validate that systems meet recognized standards like HACCP or GFSI-benchmarked schemes. This dual-layer approach ensures both internal vigilance and external credibility.
Demonstrating Due Diligence to Stakeholders
The audit process also serves as evidence of due diligence to stakeholders. Retailers, distributors, and consumers increasingly demand proof of food safety commitment. Documented audit results provide tangible evidence that a business takes its safety responsibilities seriously, opening doors to new markets and partnerships that require certified suppliers.
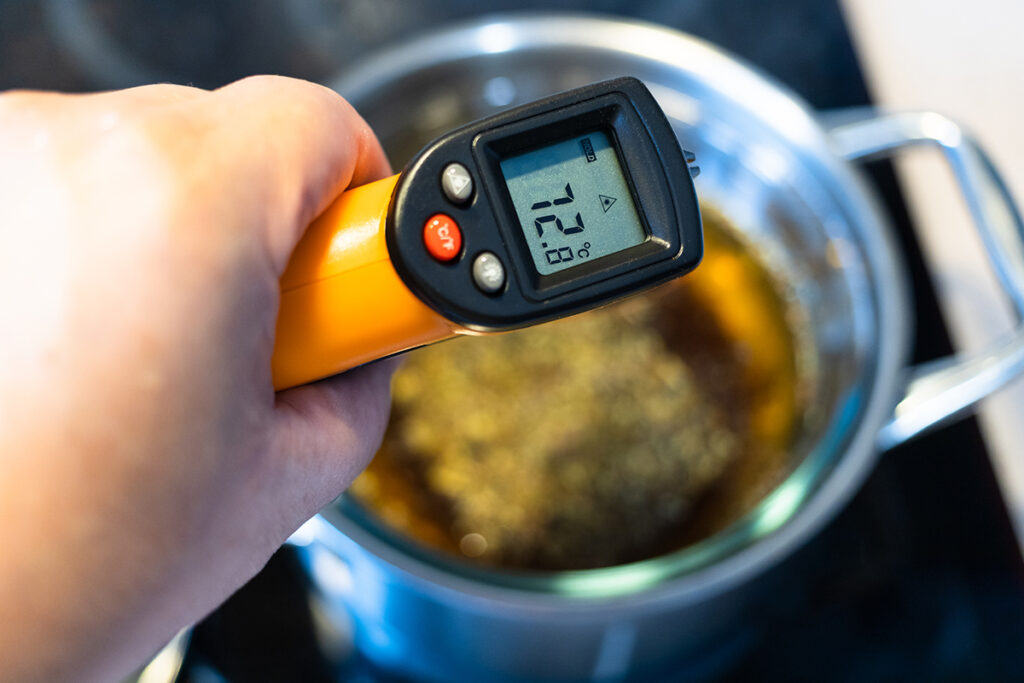

What Are the Core Components of an Effective Food Safety Management System?
An effective food safety management system relies on structured methodologies that systematically identify and control potential hazards throughout the food production chain. HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) serves as the foundation for most modern food safety management systems, providing a science-based framework that prevents, eliminates, or reduces food safety hazards to acceptable levels.
Understanding HACCP’s Role in Hazard Control
HACCP transforms food safety from reactive problem-solving to proactive risk management. The system requires food businesses to analyze every step of their operations—from raw material receipt to final product distribution—identifying where biological, chemical, or physical hazards could compromise food safety. A bakery implementing HACCP might identify metal contamination from mixing equipment, allergen cross-contact during production changeovers, or bacterial growth from inadequate cooling as critical hazards requiring specific controls.
Conducting Comprehensive Hazard Analysis
Hazard analysis forms the first pillar of any food safety management system. This process involves examining each ingredient, process step, storage condition, and handling practice to determine potential risks. Teams must consider:
- Biological hazards: Pathogens like Salmonella, Listeria, or E. coli that could contaminate products
- Chemical hazards: Cleaning agents, pesticides, or naturally occurring toxins
- Physical hazards: Glass fragments, metal shavings, or plastic pieces
- Allergen hazards: Cross-contact with major allergens during processing
The analysis evaluates both the likelihood of occurrence and potential severity of each hazard, prioritizing those requiring stringent control measures.
Identifying Critical Control Points
Critical control points (CCPs) represent specific locations, steps, or procedures where control measures can prevent, eliminate, or reduce identified hazards to safe levels. A meat processing facility might establish CCPs at cooking (to eliminate pathogens), metal detection (to remove physical hazards), and cold storage (to prevent bacterial growth). Each CCP requires clearly defined critical limits—measurable parameters that separate safe from unsafe conditions.
A cooking CCP might specify: “All chicken products must reach an internal temperature of 75°C for at least 15 seconds.” These limits derive from scientific evidence and regulatory requirements
How Do Regular Audits Support Ongoing Food Safety Compliance?
Regular audits serve as systematic checkpoints that ensure food safety systems are functioning properly and meeting regulatory requirements. The food safety audit process creates accountability through scheduled reviews that identify potential issues before they become serious compliance violations or food safety incidents.
Internal Audits vs External Audits: Understanding the Difference
Internal audits are self-assessments conducted by trained personnel within the organization, while external audits involve independent third-party auditors or regulatory inspectors who provide objective evaluation. Internal teams have a deep understanding of daily operations and can identify practical improvement opportunities. External auditors offer fresh perspectives, industry benchmarking insights, and unbiased validation that systems meet recognized standards.
The relationship between these audit types creates a layered defense strategy. Internal reviews prepare facilities for external scrutiny by identifying and resolving gaps proactively. External validation then confirms that internal controls function effectively and align with industry expectations.
How Often Should Internal Audits Occur?
Most food businesses conduct internal audits monthly or quarterly, depending on operational complexity and risk profiles. High-risk operations handling raw proteins or allergens typically audit more frequently than low-risk facilities processing shelf-stable products.
These regular intervals serve specific purposes:
- Monthly audits catch procedural drift where staff gradually deviate from established protocols
- Quarterly comprehensive reviews assess system-wide effectiveness and identify emerging trends
- Targeted audits focus on specific areas following customer complaints, near-miss incidents, or process changes
Consistent scheduling transforms audits from reactive firefighting into proactive quality assurance. Teams develop muscle memory for compliance expectations, making adherence second nature rather than a scramble before external visits.
What Do External Audits Validate?
External audits by certification bodies, regulatory agencies, or customer representatives validate that documented systems reflect actual practices. These audits assess compliance against GFSI standards such as SQF, BRCGS, or FSSC 22000, which represent globally recognized benchmarks for food safety management.
Third-party auditors evaluate five critical dimensions:
- Compliance verification: Confirming adherence to applicable regulations and certification requirements
- Process integrity: Validating that critical control points function as intended and preventive measures are effective
- Record accuracy: Reviewing documentation for consistency with operational activities and demonstrating traceability
- Hygiene assessment: Inspecting cleanliness practices at all stages of production to prevent cross-contamination risks
- Training evaluation: Assessing employee competency in food safety practices through interviews and observations
By combining internal expertise with external validation, organizations establish robust food safety cultures capable of sustaining compliance over time.
Why Is Staff Training Vital for Maintaining Food Safety Compliance?
Food safety training transforms employees from potential risk points into active defenders of compliance. Without proper employee education, even the most sophisticated food safety management systems fail at the human level where procedures meet practice. Staff who understand the “why” behind protocols consistently apply them, reducing contamination risks and audit failures.
Building a Foundation Through Continuous Education
Continuous education keeps food safety principles fresh in employees’ minds as they face daily operational pressures. A single training session during onboarding creates a false sense of security—knowledge degrades over time, procedures evolve, and regulations change.
Effective food safety training programs operate on recurring cycles:
- Monthly refreshers on critical topics like handwashing protocols and cross-contamination prevention
- Quarterly updates when procedures change or new equipment arrives
- Annual comprehensive reviews covering all aspects of the food safety management system
- Immediate training following audit findings or near-miss incidents
Real-world scenarios strengthen retention better than theoretical presentations. When staff at a seafood processing facility practice proper temperature logging with actual thermometers rather than watching videos, they develop muscle memory that persists during busy shifts.
Customizing Training to Match Operational Roles
Generic training wastes time and fails to address role-specific risks. A receiving clerk needs deep knowledge of supplier verification and temperature checks, while a sanitation worker must master chemical handling and cleaning validation techniques.
Role-specific training addresses these distinct needs:
- Production line workers: Personal hygiene, equipment sanitation, allergen awareness, proper handling techniques
- Quality assurance staff: Sampling procedures, testing protocols, documentation requirements, corrective action implementation
- Maintenance personnel: Equipment calibration, preventive maintenance schedules, food-grade lubricants, pest-proofing techniques
- Supervisors and managers: Audit preparation, record review, staff oversight, regulatory interpretation
A bakery implementing a robust food safety compliance system for audits discovered that training decorators specifically on allergen cross-contact prevention reduced incidents by 78%. The decorators learned which tools required dedicated use for allergen-free products and how to sequence production runs to minimize contamination risks.
Measuring Training Effectiveness Through Performance Indicators
Training programs require validation beyond attendance
How Must Food Safety Systems Comply with Regulations?
Food safety systems must align with specific regulatory frameworks that govern food production, handling, and distribution within their operating jurisdictions. Regulatory compliance forms the legal foundation upon which all food safety practices are built, with non-compliance potentially resulting in product recalls, facility closures, or legal penalties.
What National and International Regulations Apply to Food Safety Systems?
Businesses must navigate a complex landscape of regulations depending on their location and market reach. In the United States, the FDA FSMA (Food Safety Modernization Act) represents the most significant reform of food safety laws in over 70 years, shifting the focus from responding to contamination to preventing it. The law mandates preventive controls, establishes science-based minimum standards for produce safety, and requires foreign suppliers to meet U.S. safety standards.
Australian food businesses operate under the Food Standards Code Australia, which establishes maximum levels of contaminants, additives, and processing aids while defining labeling requirements and compositional standards. This code applies across all states and territories, creating a unified approach to food safety regulation.
International operations require adherence to Codex Alimentarius standards, which provide harmonized international food standards, guidelines, and codes of practice. The European Union’s General Food Law Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 establishes comprehensive food safety principles for businesses operating within EU markets.
What Are the Essential Regulatory Requirements for Food Safety Systems?
Hygiene protocols form the cornerstone of regulatory compliance, requiring businesses to maintain sanitary conditions throughout all stages of food production. These protocols mandate:
- Personal hygiene practices including handwashing stations, protective clothing, and illness reporting procedures
- Cleaning and sanitization schedules with documented verification
- Separation of raw and ready-to-eat products to prevent cross-contamination
- Pest control programs with regular monitoring and documentation
Temperature controls represent critical regulatory requirements across all jurisdictions. Refrigerated foods must maintain temperatures at or below 5°C (41°F), while hot foods require holding temperatures above 60°C (140°F). Cooking temperatures vary by product type, with poultry requiring internal temperatures of 74°C (165°F) and ground meats reaching 71°C (160°F).
How Can Technology Enhance Food Safety Compliance and Audit Preparation?
Digital food safety software transforms compliance management from paper-based chaos into streamlined, verifiable processes. These platforms automate routine tasks, reduce human error, and provide auditors with instant access to comprehensive records that demonstrate systematic food safety control.
Automated Checklists and Reminders
Digital checklists eliminate the risk of missed inspections or forgotten procedures. Staff receive automated notifications for scheduled tasks like temperature checks, equipment calibration, or cleaning protocols. The system timestamps each completed action and flags overdue items immediately, ensuring no critical control point goes unmonitored.
Smart reminder systems adapt to operational patterns. If a refrigeration unit requires temperature logging every four hours, the software sends alerts to designated personnel precisely when readings are due. This proactive approach prevents compliance gaps before they occur.
Centralized Document Storage
Traditional filing systems scatter critical records across multiple locations—temperature logs in one binder, cleaning schedules in another, training certificates in a third. Digital food safety software consolidates all documentation into a single, searchable repository accessible from any authorized device.
Auditors can retrieve years of records within seconds rather than hours. When an inspector requests proof of corrective actions from six months prior, staff locate the exact document with date-stamped photos, assigned responsibilities, and verification of completion. This instant traceability demonstrates organizational competence and transparency.
Cloud-based storage provides automatic backups, protecting against data loss from physical damage or system failures. Version control ensures teams always reference the most current procedures and policies.
Real-Time Monitoring Capabilities
Real-time monitoring systems track critical parameters continuously without manual intervention. IoT-enabled sensors measure refrigeration temperatures, humidity levels, or cooking times and transmit data directly to the compliance platform. Deviations from acceptable ranges trigger immediate alerts to supervisors.
This constant surveillance identifies problems at their earliest stage. A freezer temperature rising by two degrees might seem insignificant during a manual check, but continuous monitoring reveals the upward trend hours before product safety becomes compromised. Staff can address equipment malfunctions before they escalate into costly product losses or health hazards.
Photo Evidence and Geolocation Verification
Modern compliance platforms allow staff to attach timestamped photographs directly to inspection records. Visual documentation proves cleaning
What Role Do Corrective Actions Play in Strengthening Food Safety Systems?
Corrective actions are essential for continuously improving a strong food safety compliance system during audits. When auditors find issues—such as temperature problems, missing documents, or not following procedures—how quickly and effectively you respond will affect both immediate food safety and the long-term strength of your system.
Quick corrective actions stop small problems from turning into big food safety incidents. If a temperature log shows that refrigeration is not at the safe level, you need to act right away: move the affected products, investigate why the equipment failed, and document everything you did in response. If you wait too long to react, it could put the safety of your products at risk and lead to expensive recalls or penalties from regulators.
Identifying Non-Conformities During Audits
Audits can uncover weaknesses that day-to-day operations might miss. Some common issues found during audits include:
- Incomplete or missing documents for critical control points
- Staff not following established cleaning protocols
- Pest control measures that are not adequate or evidence of pest activity
- Risks of cross-contamination in storage or preparation areas
- Equipment calibration records that are outdated or absent
- Allergen management procedures not properly implemented
Each finding is an opportunity to make your food safety system stronger. Instead of viewing the audit report as a list of failures, use it as a guide for making specific improvements.
The Critical Importance of Root Cause Analysis
Fixing problems on the surface only addresses symptoms without getting to the root causes. To prevent non-conformities from happening again, you need to dig deeper and understand why they occurred.
A systematic approach to root cause analysis involves asking “why” repeatedly until reaching the fundamental issue. For example, if staff consistently fail to complete temperature logs, the surface problem may seem like negligence. However, further investigation might reveal inadequate training, confusing procedures, or thermometers placed inconveniently far from workstations.
The “5 Whys” technique is particularly effective in this process:
- Why was the temperature log incomplete? Staff member forgot to record readings.
- Why did they forget? No reminder system exists during busy service periods.
- Why is there no reminder system? Management assumed staff would remember without prompts.
- Why was this assumption made? Previous location had fewer daily temperature checks required.
- Why weren’t procedures updated for this new requirement? Management didn’t realize the impact of increased checks on staff workload.
By identifying and addressing these underlying issues through corrective actions, you can create lasting improvements in your food safety practices and reduce the likelihood of non-conformities occurring again in future audits.
Why Is Certification Important for Demonstrating Food Safety Commitment?
Certification provides third-party validation that your food safety system meets internationally recognized standards. Independent certification programs such as SQF (Safe Quality Food), BRCGS (Brand Reputation through Compliance Global Standards), and FSSC 22000 (Food Safety System Certification) offer credible proof to customers, retailers, and regulators that your organization operates according to rigorous food safety protocols.
These certifications open market access, particularly with major retailers and food service companies that require GFSI-benchmarked credentials from their suppliers. A certified facility demonstrates systematic hazard control, consistent quality management, and commitment to continuous improvement—factors that build trust with stakeholders and differentiate your business in competitive markets.
What Value Do Global Certifications Bring to Food Businesses?
Global certifications eliminate the need for multiple customer audits by providing a single, recognized credential accepted across markets. SQF certification, developed by the Food Marketing Institute, combines food safety with quality management and is widely required by North American retailers. BRCGS certification, originating from the British Retail Consortium, holds strong recognition in European markets and covers food safety, quality, and operational criteria.
FSSC 22000 integrates ISO 22000 with sector-specific prerequisite programs, creating a comprehensive framework recognized by the Global Food Safety Initiative. This certification suits manufacturers, processors, and logistics providers seeking alignment with international standards. Each certification carries different strengths:
- SQF: Emphasizes food quality alongside safety, with three certification levels
- BRCGS: Includes product safety, process control, and personnel requirements with graded scoring
- FSSC 22000: Focuses on systematic management approach with strong ISO integration
How Does the Certification Process Work?
The certification journey begins with gap analysis—a detailed assessment comparing current practices against certification requirements. This diagnostic phase identifies deficiencies in documentation, procedures, infrastructure, or training that need addressing before formal audit.

What Challenges Arise When Implementing a Robust Food Safety Compliance System?
Challenges in food safety compliance arise from the complexity of maintaining comprehensive systems that satisfy multiple stakeholders while adapting to constant industry changes. Organizations face operational, technical, and human resource obstacles that can derail even well-intentioned compliance efforts.
How Does Documentation Volume Overwhelm Food Safety Teams?
Documentation requirements create significant administrative burdens for food businesses. A typical facility must maintain records for temperature logs, cleaning schedules, equipment calibration, supplier verification, pest control activities, staff training certificates, corrective actions, and audit findings—often spanning years for regulatory purposes.
Paper-based systems amplify these challenges through physical storage limitations, difficulty retrieving specific records during audits, and increased risk of document loss or damage. Teams spend hours manually completing forms, filing paperwork, and searching through filing cabinets when auditors request evidence.
The volume intensifies as businesses scale operations or add product lines. Each new process introduces additional monitoring points, each requiring separate documentation trails. Small errors in record-keeping—missing signatures, incomplete dates, illegible handwriting—can result in audit non-conformities despite actual compliance with safety procedures.
Why Do Regulatory Changes Create Compliance Gaps?
Food safety regulations evolve continuously as scientific understanding advances and new hazards emerge. Regulatory bodies update standards for pathogen control, allergen labeling, sanitation protocols, and traceability requirements with varying implementation timelines.
Businesses struggle to monitor multiple regulatory sources simultaneously. A company exporting internationally must track FDA requirements, EU regulations, destination country standards, and customer-specific certification schemes. Missing a single regulatory update can render existing procedures non-compliant overnight.
The interpretation of new regulations presents additional complications. Vague regulatory language leaves room for different understandings of compliance requirements. Food safety managers must determine how broad directives apply to their specific operations, products, and processes without clear guidance until enforcement actions clarify expectations.
What Resistance Hinders Procedure Implementation?
Staff resistance to new protocols creates implementation barriers across organizational levels. Production workers accustomed to established routines view additional documentation steps as productivity obstacles. Supervisors resist changing familiar processes that have “always worked fine” despite lacking formal hazard controls.
Cultural factors influence compliance attitudes differently across facilities. Long-tenured employees may
Conclusion
Implementing a strong food safety compliance system for audits turns regulatory requirements into competitive advantages. Organizations that focus on systematic hazard control, regular auditing cycles, and continuous staff development position themselves as industry leaders rather than just compliance checkers.
An effective food safety compliance system relies on continuous improvement. Each audit cycle uncovers opportunities to strengthen protocols, each training session deepens organizational knowledge, and each technological integration enhances traceability. Successful businesses see compliance as an ongoing journey that requires constant attention and resource allocation.
The way forward requires three key commitments:
- Embrace technology to reduce documentation burdens and improve real-time monitoring capabilities
- Invest in people through ongoing training programs that adapt to emerging risks and regulatory shifts
- Maintain vigilance by treating every audit as a learning opportunity rather than a pass-fail examination
Food safety systems that include these principles create resilient frameworks capable of withstanding regulatory scrutiny while protecting public health. The initial investment in comprehensive processes, digital tools, and certification programs pays off through reduced recall risks, enhanced brand reputation, and streamlined audit experiences.
Success requires leadership commitment beyond compliance departments. When food safety becomes part of the organizational culture—from executive decision-making to frontline operations—businesses become agile in responding to new hazards, regulatory changes, and consumer expectations. This cultural shift transforms compliance from a cost center into a value generator that builds consumer trust and operational excellence.
Organizations that succeed in today’s complex food safety landscape understand that strong systems need constant care. Regular system reviews, proactive gap analyses, and willingness to adapt procedures ensure compliance frameworks stay relevant and effective as the industry evolves.
Click here for more The Link Between Food Safety and Compliance in Manufacturing
SEO Marketing: The Ultimate Guide to Australian Business Growth
The digital landscape in Australia is uniquely competitive. From the bustling tech hubs of Sydney and Melbourne to the localized markets of Perth and Brisbane, seo marketing has evolved from a luxury to a fundamental necessity for survival. For Australian businesses, appearing on the first page of Google isn’t just about vanity; it is about capturing high-intent traffic at the exact moment a customer is ready to convert.
Whether you are a national enterprise or a neighborhood service provider, understanding the mechanics of search engine optimization is the key to sustainable, organic growth. This guide breaks down the complexities of modern SEO, specifically tailored for the Australian market.
What is SEO Marketing?
SEO marketing is the strategic process of optimizing a website to increase its visibility in organic search engine results pages (SERPs). Unlike paid advertising (SEM), SEO focuses on “earned” traffic. By aligning your website with Google’s sophisticated algorithms, you ensure that your content is discovered, crawled, and indexed as the most authoritative answer to a user’s query.
In the Australian context, this involves a blend of technical excellence, high-quality content creation, and a deep understanding of local search behavior.
The Core Pillars of Modern SEO
- Technical SEO: Ensuring search engines can crawl and index your site without friction.
- On-Page SEO: Optimizing individual pages, including meta tags, headers, and content quality.
- Off-Page SEO: Building the site’s reputation through high-authority backlinks and social signals.
- Content Strategy: Creating value-driven information that satisfies the user’s search intent.
Why SEO Marketing is Essential for Australian Businesses
The Australian consumer path to purchase almost always begins with a search query. With Google holding over 94% of the search engine market share in Australia, “SEO” effectively means “Optimizing for Google.”
Compounding Long-Term Value
Unlike PPC (Pay-Per-Click), where traffic stops the moment you stop paying, SEO is an investment in an asset. A well-optimized page continues to generate leads years after its initial publication.
Cost-Effectiveness
While SEO requires an upfront investment in time or agency fees, the cost per acquisition (CPA) is significantly lower over time compared to traditional media or digital ads.
Building Trust and Authority (E-E-A-T)
Google prioritizes Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Ranking highly signals to Australian consumers that your brand is a leader in your industry.
Local SEO for Small Business Growth
For many Australian companies, the most immediate ROI comes from local SEO for small business growth. This is the practice of optimizing your online presence to attract more business from relevant local searches.
The Power of the “Map Pack”
When an Aussie searches for “electrician near me” or “best cafe in Adelaide,” Google displays the “Local Pack” (the map and three business listings). Securing a spot here is transformative.
| Local SEO Element | Impact on Growth |
| Google Business Profile (GBP) | Increases visibility on Google Maps and local search. |
| Local Citations | Ensures NAP (Name, Address, Phone) consistency across directories like Yellow Pages and TrueLocal. |
| Customer Reviews | Builds social proof and improves local ranking signals. |
| Geo-Targeted Content | Helps Google associate your services with specific Australian suburbs or regions. |
The Step-by-Step SEO Marketing Framework
Success in SEO isn’t accidental. It requires a logical, data-driven approach. Follow this framework to build a high-performing SEO engine.
Phase 1: Comprehensive Keyword Research
Don’t guess what your customers are typing. Use tools to find “seed keywords” and long-tail phrases. Look for:
- Search Volume: How many people are searching for this in Australia?
- Keyword Difficulty: How hard is it to outrank the current competition?
- Search Intent: Is the user looking for information, a specific brand, or a product to buy?
Phase 2: Technical Site Audit
Google won’t rank a site it can’t understand.
- Mobile-First Indexing: Your site must perform flawlessly on mobile devices.
- Site Speed: Aim for a “Good” rating in Core Web Vitals.
- HTTPS: Security is a non-negotiable ranking factor.
- XML Sitemaps: Provide a roadmap for Google’s spiders.
Phase 3: Content Creation and Optimization
Write for humans first, but keep search engines in mind. Use a clear hierarchy:
- H1 Tags: Include your primary keyword.
- H2-H3 Subheadings: Use these to break up content and address LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords.
- Internal Linking: Link to other relevant pages on your site to distribute “link equity.”
Phase 4: Quality Backlink Acquisition
A backlink is a vote of confidence. Focus on getting links from reputable Australian domains (.com.au, .net.au, .org.au) to boost your local relevance.
Advanced SEO Best Practices
To stay ahead of the competition in the Australian SERPs, you must look beyond the basics.
1. Optimize for Featured Snippets
Aim for “Position Zero” by providing clear, concise answers to common questions within your content. Use bulleted lists and short, 40-50 word definitions.
2. Focus on “Topic Clusters”
Instead of targeting isolated keywords, build a “pillar page” that covers a broad topic and link it to several “cluster pages” that dive deep into specific sub-topics. This establishes topical authority.
3. Leverage Schema Markup
Schema is a form of microdata that helps Google understand the context of your content. Implementing “LocalBusiness” or “Product” schema can result in rich snippets (stars, prices, and event dates) that increase your click-through rate (CTR).
Common SEO Mistakes to Avoid

- Keyword Stuffing: Overusing your primary keyword feels unnatural to readers and triggers spam filters.
- Ignoring User Experience (UX): If your site is hard to navigate or has intrusive pop-ups, users will “bounce,” telling Google your site isn’t valuable.
- Duplicate Content: Copying descriptions from manufacturers or other sites hurts your rankings. Always provide original insights.
- Neglecting Mobile Users: With a high percentage of Australians browsing on the go, a desktop-only mindset is a recipe for failure.
FAQ: SEO Marketing in Australia
What is the difference between SEO and SEM?
SEO focuses on earning traffic through organic, non-paid rankings. SEM (Search Engine Marketing) typically refers to paid strategies like Google Ads to gain visibility.
How long does it take to see results from SEO?
Generally, it takes 3 to 6 months to see significant movement in rankings. SEO is a long-term strategy that builds momentum over time.
Why is local SEO for small business growth so important?
Local SEO targets customers in your immediate geographic area. It has a higher conversion rate because it captures users with high “near-me” intent who are often ready to visit or call a business immediately.
Does social media affect my SEO?
Social media does not directly impact your search rankings. However, it increases brand awareness and can lead to more mentions and backlinks, which do help SEO.
How often should I update my content?
Content should be reviewed at least every 6-12 months. Updating old posts with fresh data, new links, and current trends can provide a significant “ranking boost.”
Do I need a professional for SEO marketing?
While basic SEO can be done in-house, professional strategists understand the technical nuances and algorithm shifts that can make or break a digital presence.
Conclusion: The Path to Search Dominance
SEO marketing is no longer just about “tricking” an algorithm; it is about providing the best possible experience and most relevant information to your audience. By focusing on technical health, high-quality content, and local SEO for small business growth, Australian companies can build a resilient digital presence that outlasts any algorithm update.
Food Safety Temperature Monitoring: How to Prevent Spoilage and Equipment Failure
What Is Food Safety Temperature Monitoring and Why Is It Important?
Food safety temperature monitoring tracks and records temperatures in refrigeration units, freezers, and food storage areas to ensure products remain within safe ranges. This process uses sensors and digital systems to continuously measure conditions where perishable items are stored.
Continuous monitoring is crucial for preventing spoilage and equipment failure in foodservice operations. Unlike periodic manual checks, modern temperature monitoring systems collect data every 1-5 minutes, creating a comprehensive safety net that catches deviations before they compromise food quality or equipment integrity.
The importance of food safety temperature monitoring in food safety cannot be overstated. When temperatures drift outside safe zones—typically 40°F (4°C) or below for refrigeration and 0°F (-18°C) for freezers—bacterial growth accelerates rapidly, rendering food unsafe for consumption.
Neglecting temperature control carries severe consequences:
- Financial losses ranging from thousands to tens of thousands of dollars per incident due to spoiled inventory
- Health risks from foodborne illness outbreaks that can harm customers and damage reputation
- Regulatory violations resulting in fines, failed inspections, or temporary closures
- Emergency repair costs when equipment failures go undetected until complete breakdown occurs
- Revenue loss during operational downtime while replacing spoiled inventory and repairing equipment
Approximately 60% of restaurants experience food spoilage due to equipment failure annually, making proactive temperature monitoring an essential investment rather than an optional expense.
What Are the Common Causes of Food Spoilage and Equipment Failure in Foodservice Operations?
Refrigeration equipment failure is the main reason why food goes bad in commercial kitchens. Around 60% of restaurants experience spoilage incidents every year because their cooling systems are not working properly. Each incident can cost anywhere from thousands to tens of thousands of dollars.
The most common reasons for food spoilage are specific mechanical breakdowns:
- Compressor problems that stop the cooling cycles from working
- Worn-out door seals that let warm air in
- Refrigerant leaks that reduce the cooling power
- Thermostat issues that cause incorrect temperature readings
- Blocked condenser coils that prevent heat from being released
These failures lead to a chain reaction of financial consequences. The first blow is the loss of inventory—emergency repair costs, revenue loss during downtime, and replacement food purchases add to the damage. Just one failure in a walk-in cooler can ruin $10,000 worth of perishable ingredients overnight.
Health risks and regulatory violations make the situation even more serious than just losing money. Spoiled food with bacteria like Salmonella, Listeria, or E. coli can endanger customers’ health. Health departments impose fines for not controlling temperatures, and in severe cases, they can order temporary closures. If there are outbreaks of foodborne illnesses, it can harm a restaurant’s reputation permanently and threaten its survival. That’s why it’s crucial to have reliable monitoring systems in place to prevent such incidents rather than considering them as optional measures.
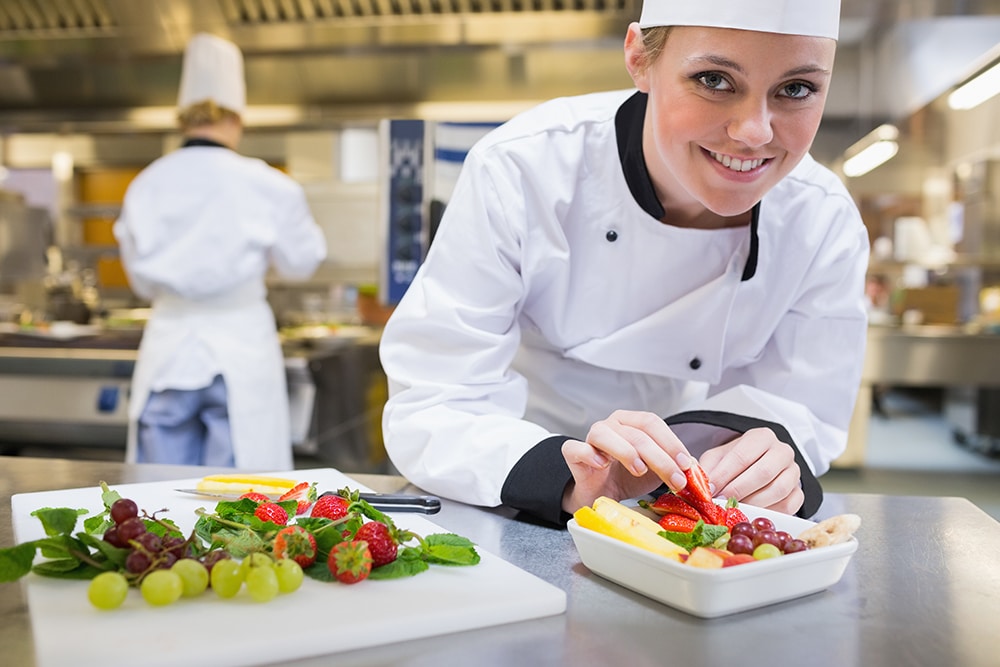

Why Are Traditional Manual Temperature Checks Inadequate?
Manual temperature checks create dangerous gaps in monitoring because they only capture snapshots at specific moments, typically 2-3 times daily. A refrigeration unit can experience temperature fluctuations at any time—during overnight hours, weekends, or between scheduled checks—leaving food vulnerable to spoilage for hours before detection.
Human error in monitoring compounds these limitations through several common scenarios:
- Staff members forgetting to perform checks during busy service periods
- Recording temperatures incorrectly or rounding numbers for convenience
- Writing down readings without actually taking measurements
- Losing paper logs or failing to maintain organized records
- Misreading analog thermometers or using uncalibrated equipment
The manual temperature checks limitations extend beyond timing issues. Even diligent employees cannot detect gradual temperature increases that signal impending equipment failure. A compressor struggling to maintain proper cooling might raise internal temperatures by just one degree per hour—imperceptible during a quick check but catastrophic over an eight-hour shift.
Moreover, the challenges posed by paper-based record keeping present additional obstacles for health inspections. Handwritten logs are difficult to verify, easy to fabricate after the fact, and provide no proof that temperatures remained stable between recorded measurements. Health departments increasingly question the reliability of manual documentation, recognizing these systems cannot guarantee continuous compliance with food safety regulations.
How Do IoT Sensors Improve Temperature Monitoring?
IoT temperature sensors collect data points every 1-5 minutes, creating a comprehensive temperature profile that captures every fluctuation in refrigeration units. These wireless devices transmit readings automatically to cloud-based platforms without requiring staff intervention.
The technology transforms Food Safety Temperature Monitoring: How to Prevent Spoilage and Equipment Failure through several key capabilities:
1. Data Collection Frequency
- Sensors record temperatures 288-1,440 times per day compared to 2-3 manual checks
- Continuous temperature monitoring detects deviations within minutes rather than hours
- Historical data reveals patterns that indicate developing equipment issues
2. Accuracy Advantages
IoT temperature sensors eliminate the guesswork inherent in manual logging. Digital readings provide precise measurements to decimal points, removing subjective interpretation of analog thermometers. Each sensor undergoes factory calibration to ensure consistent accuracy across all monitoring points.
3. Operational Reliability
The automated nature of IoT systems means temperature tracking continues during busy service periods, overnight hours, and weekends when manual checks typically lapse. Sensors operate independently of staff schedules, ensuring no gaps in surveillance regardless of labor shortages or shift changes.
4. Multi-Point Monitoring
A single system can track dozens of refrigeration units, freezers, and storage areas simultaneously. This scalability proves impossible with manual methods, where checking multiple locations consumes significant labor hours while still leaving blind spots between inspections.
What Are the Benefits of Cloud-Based Temperature Monitoring Systems?
Cloud-based monitoring benefits transform raw sensor data into actionable intelligence that protects food inventory and business operations. These platforms receive temperature readings from IoT devices and analyze them against preset thresholds, triggering real-time alerts food safety managers need to respond immediately when conditions drift outside safe zones.
The notification system operates through multiple channels simultaneously:
- SMS text messages reach staff instantly on mobile devices
- Email alerts provide detailed temperature deviation reports
- Phone calls escalate critical situations requiring urgent attention
- Mobile app push notifications deliver updates to designated personnel
Response times shrink from hours to minutes, allowing teams to address malfunctioning equipment or improperly closed doors before spoilage occurs. A walk-in cooler climbing from 38°F to 45°F triggers immediate warnings, enabling corrective action while food remains safe.
Automatic logging for health department compliance eliminates manual temperature record-keeping entirely. The system generates timestamped documentation of every reading, creating audit-ready reports that satisfy regulatory requirements. Health inspectors receive comprehensive temperature histories spanning weeks or months, demonstrating consistent adherence to food safety protocols.
These platforms operate independently through cellular connectivity, maintaining surveillance even during internet outages or power disruptions. The redundancy ensures uninterrupted protection regardless of on-site infrastructure challenges, with backup power keeping sensors active during emergencies.
How Does Temperature Monitoring Help Prevent Equipment Failures?
Can temperature data predict when refrigeration equipment will fail? Continuous monitoring systems detect subtle temperature fluctuations that signal impending equipment problems, enabling predictive maintenance foodservice operations to schedule repairs before catastrophic failures occur.
Early detection of equipment issues saves restaurants from costly emergency repairs and inventory losses. IoT sensors identify specific problems through characteristic temperature patterns:
- Compressor degradation: Gradual temperature increases over several days indicate declining compressor efficiency, allowing scheduled replacement during off-hours rather than mid-service breakdowns
- Door seal failures: Frequent temperature spikes during operating hours reveal compromised gaskets that force refrigeration units to work harder, increasing energy costs and wear
- Refrigerant leaks: Steady upward temperature drift combined with longer compressor run times signals refrigerant loss requiring immediate attention
The system’s historical data reveals equipment performance trends invisible to manual checks. A walk-in cooler maintaining 38°F instead of the optimal 35°F might pass a quick manual inspection but indicates developing issues. Addressing these problems early extends equipment lifespan by years and prevents the cascade of failures that occur when one compromised unit forces others to compensate.
Maintenance teams receive detailed temperature graphs showing exactly when anomalies began, helping technicians diagnose problems faster and reducing diagnostic costs by 30-40% compared to reactive service calls.
Can Temperature Monitoring Contribute to Energy Savings?
Refrigeration accounts for 30-40% of a restaurant’s total energy consumption, making it one of the largest operational expenses. Continuous temperature monitoring identifies inefficiencies that drive up utility costs, revealing patterns invisible to manual checks.
Energy savings refrigeration systems benefit from constant data collection that exposes several costly issues:
- Temperature cycling patterns that indicate compressors working harder than necessary
- Frequent on-off cycles suggesting thermostat calibration problems
- Gradual temperature drift pointing to deteriorating insulation or seal integrity
- Baseline deviations across similar units revealing underperforming equipment
When sensors detect a walk-in cooler maintaining 36°F instead of the optimal 38°F, the compressor runs unnecessarily, consuming 5-10% more energy. This seemingly minor two-degree difference translates to hundreds of dollars annually per unit.
Optimized HVAC operation extends beyond refrigeration. Temperature data helps identify units cycling excessively during off-peak hours or struggling to maintain setpoints—both indicators of maintenance needs or efficiency losses. Addressing these issues before they escalate prevents the energy waste associated with degraded performance.
The granular data from IoT sensors enables facility managers to benchmark performance across multiple units and locations. A refrigerator consistently drawing more power than identical models flags itself for inspection, allowing targeted interventions that reduce energy consumption by 15-25% after corrective maintenance.
What Are the Operational Advantages Beyond Safety and Compliance?
Operational efficiency foodservice improvements extend far beyond preventing spoilage. Cloud-based temperature monitoring eliminates the need for staff to manually check and log temperatures multiple times per shift, freeing up labor hours for customer-facing activities. A single manager can monitor dozens of refrigeration units across an entire facility from one dashboard, reducing time spent on routine inspections by 75%.
Multi-location management systems transform how restaurant chains and franchise operations maintain consistency. Operators can view real-time temperature data from every location simultaneously, identifying which sites need attention without making phone calls or site visits. This centralized visibility allows corporate teams to spot patterns—such as recurring equipment issues at specific locations—and deploy maintenance resources strategically.
The data collected creates accountability through transparent records accessible to both on-site staff and regional managers. When temperature excursions occur, the system timestamps exactly when the deviation started, how long it lasted, and which team members received alerts. This documentation supports training initiatives by highlighting response times and corrective actions taken.
Remote monitoring capabilities prove particularly valuable during off-hours. Rather than requiring staff to physically check equipment after closing, managers receive automated reports confirming all units maintained proper temperatures overnight. Any issues trigger immediate alerts, allowing problems to be addressed before the morning shift arrives.

How Is Food Safety Temperature Monitoring Implemented in Practice?
Does setting up temperature monitoring disrupt daily operations? The installation wireless sensors process takes minimal time and causes virtually no interruption to business activities. Technicians mount wireless sensors directly onto refrigeration units, freezers, and other critical equipment without requiring modifications to existing infrastructure. The entire setup typically completes within a few hours, allowing restaurants to continue normal service throughout the process.
What does the deployment process involve? Installation teams position sensors at strategic points inside coolers and freezers, securing them with adhesive mounts or magnetic attachments. Each sensor connects to a cellular gateway that transmits data independently of the restaurant’s internet network, eliminating dependency on Wi-Fi reliability. The cloud platform automatically begins collecting temperature readings once sensors activate.
How quickly can staff start using the system? Staff training on alerts system takes approximately 30 minutes to an hour. Employees learn to:
- Access the dashboard from smartphones, tablets, or computers
- Interpret temperature readings and alert notifications
- Respond appropriately to different alert levels
- Document corrective actions taken
- Generate compliance reports for health inspections
The user interface presents information through color-coded displays and straightforward navigation, making it accessible even for team members with limited technical experience. Managers receive credentials to customize alert thresholds, assign notification recipients, and monitor multiple locations from a single centralized platform.
Conclusion
Continuous IoT-based monitoring changes food safety from dealing with crises after they happen to stopping risks before they occur. The benefits of temperature monitoring food safety go beyond just following rules—protecting your stock, reputation, and profits while avoiding health risks that could seriously harm your business.
Food Safety Temperature Monitoring: How to Prevent Spoilage and Equipment Failure isn’t just about technology; it’s about being strong in operations. Every minute that temperature changes without anyone knowing puts your business in danger. Modern monitoring systems offer the constant watchfulness that manual checks can’t provide, finding problems before they turn into expensive emergencies.
Take a look at how you currently monitor temperatures. Does it send alerts instantly? Can it stop the next equipment failure? Look into solutions made for your specific operational needs today.
Click here for more Remote Temperature Monitoring Australia: How It Works for Multi-Location Food Brands
Remote Temperature Monitoring Australia: How It Works for Multi-Location Food Brands
What is Remote Temperature Monitoring and How Does It Work?
Remote temperature monitoring is an automated system that tracks and records temperatures across refrigeration units, freezers, and warming equipment without manual intervention. These systems use wireless sensors placed inside cold storage units to continuously measure temperature levels and transmit data to cloud-based platforms accessible from anywhere.
The technology eliminates the traditional clipboard-and-pen approach to temperature logging. Instead of staff members manually checking and recording temperatures multiple times per day, wireless sensors do this work automatically and with greater accuracy.
How Wireless Sensors Capture Temperature Data
The core of any remote temperature monitoring Australia system consists of small, wireless sensors installed in refrigerators, freezers, and warmers. These devices contain precision thermometers that measure ambient temperatures within the storage unit.
Each sensor connects to a gateway device—typically mounted on a wall or placed in a central location within the facility. The gateway acts as a communication hub, collecting data from multiple sensors and transmitting it to the cloud via Wi-Fi or cellular networks.
The sensors operate continuously, taking temperature readings at regular intervals. Most systems in Australia capture data every 10 minutes, creating a detailed temperature profile throughout the day and night. This frequency ensures that any temperature fluctuations—even brief ones—are detected and recorded.
Real-Time Data Updates Through Dashboard Access
Temperature data flows to secure online dashboards where authorized users can view current and historical readings. These dashboards display information in easy-to-read formats, including:
- Live temperature readings for each monitored unit
- Temperature trend graphs showing patterns over hours, days, or weeks
- Status indicators highlighting which units are operating within safe ranges
- Alert notifications when temperatures breach preset thresholds
The real-time nature of these updates means managers can check conditions at any moment. Whether sitting in a head office reviewing multiple locations or standing in a kitchen checking a specific freezer, the data is identical and current.
Multi-Location Accessibility Features
For food brands operating across multiple sites, remote temperature monitoring systems provide centralized visibility. A single dashboard can display data from dozens or hundreds of locations simultaneously. This consolidated view allows:
- Regional managers to monitor all sites within their territory
- Quality assurance teams to verify compliance across the entire network
- Maintenance staff to identify equipment issues before they cause failures

Why is Remote Temperature Monitoring Essential for Multi-Location Food Brands?
Multi-location food brands face significant challenges when it comes to manually managing temperature compliance across multiple sites. Each additional location increases the risk of human error, missed temperature checks, and inconsistent record-keeping that can jeopardize food safety compliance Australia standards.
The Challenges of Manual Management
Operating restaurants, cafes, or food retail chains in different suburbs or states presents logistical difficulties that manual systems cannot effectively handle. Staff members at each location must remember to check and log temperatures multiple times a day, resulting in numerous individual data points that need verification. When a regional manager oversees 10, 20, or 50 locations, it becomes impossible to physically visit each site to verify temperature logs.
Manual temperature logging has several critical weaknesses:
- Inconsistent checking schedules between locations due to varying staff diligence
- Illegible handwritten records that complicate audits and compliance verification
- Missed temperature readings during busy service periods or staff shortages
- Delayed detection of equipment malfunctions that could spoil entire inventories
- No visibility into temperature conditions during overnight hours or weekends
A single missed temperature check at one location could lead to spoiled stock worth thousands of dollars. When you consider this risk across multiple sites, the potential for significant financial loss becomes substantial.
Meeting Australian Food Safety Standards Across Every Location
Australian food safety regulations require strict temperature compliance for different food categories. The Food Standards Code mandates businesses to keep cold food at 5°C or below and hot food at 60°C or above, with specific requirements varying by food type. Ensuring every location in different states—each potentially subject to local health department inspections—maintains these standards simultaneously requires systematic oversight.
Multi-location food management becomes especially challenging when:
- Different sites have varying equipment ages and reliability levels
- Staff turnover rates differ between locations, affecting training consistency
- Local health inspectors may arrive unannounced at any location
- Regional temperature variations impact equipment performance
- Franchise or licensed operators manage some locations independently
Remote monitoring systems establish standardized compliance protocols that apply uniformly across all sites. When the system is programmed with temperature standards, every location operates under the same parameters regardless of staff experience or local conditions.
How Do These Systems Ensure Compliance with Australian Food Safety Regulations?
Remote temperature monitoring systems ensure compliance with food safety regulations in Australia by automatically tracking and documenting the temperature of food storage units. This eliminates the need for manual checks and reduces the risk of human error.
Maintaining Temperature-Critical Zones for Different Food Types
The sensors installed in refrigeration and warming equipment record temperature readings every 10 minutes, creating a detailed log that proves consistent maintenance of temperature-critical zones. Different food categories demand distinct storage conditions: raw meats, dairy products, seafood, and prepared meals each have specific temperature thresholds that prevent bacterial growth and preserve quality.
When a refrigeration unit begins drifting outside safe parameters—even by a single degree—the system detects this deviation immediately. This precision matters because pathogenic bacteria like Salmonella and Listeria multiply rapidly in the “danger zone” between 5°C and 60°C. The continuous monitoring creates an unbroken chain of temperature documentation that health inspectors recognize as reliable evidence of proper food handling practices as outlined in the Australian Food Safety Practices.
Multi-location brands benefit particularly from this standardization. A restaurant chain with 15 locations can ensure every site maintains identical temperature standards, eliminating the inconsistency that comes with manual monitoring where different staff members might interpret requirements differently or record readings at irregular intervals.
Automated Daily and Weekly Reporting Features
Automated reporting transforms compliance from a labor-intensive task into a streamlined process. The system generates comprehensive daily reports showing minimum, maximum, and average temperatures for each monitored unit, delivered directly to designated email addresses or accessible through cloud dashboards.
Weekly summary reports provide broader trend analysis, highlighting any recurring issues such as equipment that consistently runs at the upper limit of safe ranges. These reports include:
- Time-stamped temperature readings for every monitored unit
- Visual graphs showing temperature fluctuations throughout each day
- Highlighted alerts indicating when temperatures exceeded safe thresholds
- Duration of any temperature breaches
- Automated calculations of compliance percentages
Food safety managers can schedule these reports to arrive before business hours, allowing them to proactively address any potential issues before they impact operations or customer safety.
What Are the Key Features That Support Operational Efficiency?
Remote temperature monitoring systems deliver operational efficiency through three core capabilities: instant automated alerts, elimination of manual temperature logging, and proactive energy cost management. These features work together to transform how multi-location food brands manage their cold chain operations across Australia.
Automated Alerts That Enable Immediate Response
Automated alerts form the backbone of operational efficiency in remote temperature monitoring. When a refrigerator or freezer deviates from its safe temperature range, the system instantly sends notifications through multiple channels—SMS, email, and mobile app push notifications. This multi-channel approach ensures that the right person receives the alert regardless of their location or preferred communication method.
The alert system operates 24/7, monitoring temperature readings every 10 minutes. A restaurant manager might receive an SMS at 2 AM warning that a walk-in freezer has risen to -10°C instead of the required -18°C. This immediate notification allows for quick action—whether that means calling a refrigeration technician, transferring stock to backup units, or adjusting equipment settings remotely.
Multi-location brands can customize alert thresholds for different equipment types and food categories. A butcher shop storing raw meat requires different temperature parameters than a café storing dairy products. The system accommodates these variations, sending alerts only when specific thresholds are breached for each location and storage unit.
Alert escalation protocols add another layer of efficiency. If the primary contact doesn’t acknowledge an alert within a set timeframe, the system automatically notifies secondary contacts. This ensures no critical temperature breach goes unaddressed, even during staff changeovers or busy service periods.
Elimination of Manual Temperature Logging
Manual temperature logging consumes significant staff time across multiple locations. A typical food business might require employees to check and record temperatures three times daily for each refrigeration unit. For a brand operating 10 locations with 5 units per site, this represents 150 manual checks daily—over 4,500 checks monthly.
Remote temperature monitoring eliminates this labour-intensive process entirely. Wireless sensors automatically record temperatures every 10 minutes, creating a continuous digital record without any staff intervention. Kitchen teams can focus on food preparation and customer service rather than walking between units with clipboards and thermometers.
The time savings extend beyond the actual temperature checks. They also free up resources that can be redirected towards more strategic tasks such as proactive energy cost management, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency across all locations.
How Do Remote Temperature Monitoring Systems Help Reduce Food Waste and Stock Loss?
Remote temperature monitoring systems directly combat food waste by catching temperature deviations within minutes of occurrence. When a refrigerator malfunctions at 2 AM or a freezer door stays ajar after closing time, the system immediately alerts designated staff members, enabling intervention before products reach unsafe temperatures or spoil completely.
The Speed Advantage in Spoilage Prevention
Traditional manual checks create dangerous gaps in monitoring—a refrigerator could fail at 6 PM and remain undetected until staff arrive the next morning at 8 AM. During those 14 hours, thousands of dollars in inventory could be lost. Automated systems eliminate this blind spot by sending instant notifications the moment temperatures drift outside safe parameters. A café chain in Melbourne reported saving over $45,000 annually in stock loss after implementing remote monitoring, primarily because staff could respond to equipment failures within 20-30 minutes rather than discovering spoiled products hours later.
The notification hierarchy allows businesses to escalate alerts when initial contacts don’t respond. If the store manager doesn’t acknowledge a freezer alarm within 15 minutes, the system automatically notifies the area manager, then the operations director. This redundancy ensures someone always takes timely corrective actions, regardless of time or day.
Preventing Gradual Temperature Creep
Not all stock loss comes from dramatic equipment failures. Gradual temperature increases—perhaps from a worn door seal or an overworked compressor—can compromise food quality without triggering obvious warning signs. Remote monitoring tracks temperature trends over time, identifying when a cool room consistently runs 1-2 degrees warmer than optimal. This early detection allows maintenance teams to service equipment before it fails completely, preventing both sudden stock loss and the gradual degradation that shortens product shelf life.
A Sydney-based restaurant group discovered their seafood cooler was cycling between 2°C and 6°C rather than maintaining a steady 3°C. While never reaching dangerous levels, this inconsistency was reducing their fresh fish shelf life by 24-36 hours. After the monitoring system flagged the pattern, technicians replaced a faulty thermostat, immediately improving product longevity and reducing weekly seafood orders by 12%.
Quantifying Waste Reduction Strategies
How Can These Systems Be Accessed and Managed Across Multiple Locations?
Remote temperature monitoring systems provide centralized, cloud-based access that allows multi-location food brands to view and manage all their sites from a single platform. Sensor dashboards consolidate temperature data from every refrigerator, freezer, and warmer across different locations into one unified interface, eliminating the need to physically visit each site or juggle multiple systems.
The online dashboard serves as a command center where managers can monitor real-time temperature readings, review historical data trends, and identify potential issues before they escalate. Each location appears as a separate entity within the system, yet all information flows into one accessible view. This centralized approach means a quality assurance manager in Sydney can simultaneously monitor a restaurant in Melbourne, a processing facility in Brisbane, and a storage warehouse in Perth without leaving their desk.
Real-Time Visibility Through Cloud-Based Monitoring
Cloud-based monitoring ensures temperature data uploads automatically to secure servers every 10 minutes, making information immediately available to authorized users regardless of their physical location. The system operates continuously in the background, collecting and transmitting readings without requiring manual intervention. Users simply log into their account through any web browser to access current temperatures, historical records, and compliance reports.
The cloud infrastructure provides several advantages for multi-site operations:
- Instant data synchronization across all locations
- Automatic software updates without on-site technical support
- Scalable storage for historical temperature records
- Secure access controls allowing different permission levels for staff members
- Backup redundancy protecting critical compliance data
Mobile App Convenience for On-the-Go Management
Mobile app access transforms how food brand managers oversee temperature compliance across their network. The dedicated smartphone applications mirror the functionality of desktop dashboards while adding the flexibility of monitoring from anywhere at any time. A regional manager conducting site visits can check temperatures at other locations during their commute, while on holiday, or between meetings.
The mobile interface displays the same real-time temperature data as the web dashboard but optimizes the layout for smaller screens. Users can quickly swipe between locations, zoom into specific equipment, and review alert histories with a few taps. Push notifications arrive directly on mobile devices, ensuring critical temperature breaches receive immediate attention even when managers are not physically present at the site.
The effectiveness of these remote monitoring systems is supported by various studies highlighting their impact on operational efficiency and compliance adherence in industries such as food safety. For instance, research has shown that the implementation of such technology significantly improves temperature compliance, thereby reducing instances of spoilage or health violations. Additionally, the continuous monitoring aspect has been linked to better overall management practices within food processing facilities.
How Is Continuous Monitoring Maintained During Power Outages or Business Closures?
Battery-backed gateways ensure uninterrupted data collection even when power fails or sites close for the night. These specialized devices maintain sensor connectivity and continue transmitting temperature readings to cloud-based systems, preventing critical gaps in compliance records that could expose food brands to regulatory risks.
The technology addresses a vulnerability that manual monitoring cannot solve: what happens when no staff are present to check temperatures? Power outages at 2 AM or equipment failures during weekend closures can compromise thousands of dollars in inventory within hours. Battery-backed systems eliminate this blind spot by maintaining continuous surveillance regardless of external circumstances.
How Battery-Backed Technology Functions
The gateway devices act as communication hubs between wireless temperature sensors and cloud platforms. When mains power cuts out, internal batteries automatically activate without interrupting data transmission. Most commercial-grade gateways provide 24-48 hours of backup power—sufficient coverage for typical outage durations in Australian metropolitan and regional areas.
This backup capability means temperature data continues flowing to dashboards every 10 minutes exactly as it would during normal operations. Site managers receive the same real-time alerts about temperature deviations whether the building has power or not. The system doesn’t distinguish between operational hours and closures; it simply maintains its monitoring schedule without human intervention.
Business Continuity During Extended Closures
Multi-location food brands face particular challenges during public holidays, weekend closures, or unexpected shutdowns. A restaurant chain with 30 locations cannot feasibly station staff at every site during Christmas Day just to check fridge temperatures. Remote Temperature Monitoring Australia systems solve this operational puzzle by providing constant oversight without labour costs.
The automated nature of these systems means business continuity extends beyond just data collection. Alerts still reach designated managers’ phones at 3 AM if a freezer malfunctions. The difference between catching a temperature breach at hour one versus hour twelve often determines whether stock can be salvaged or must be discarded. Battery backup ensures that critical first alert never gets missed due to power infrastructure issues.
Protection Against Data Loss
Compliance audits require complete, unbroken temperature records for specified periods—often 90 days or longer under Australian food safety standards. A single gap in data logging can trigger audit failures or raise questions about food safety
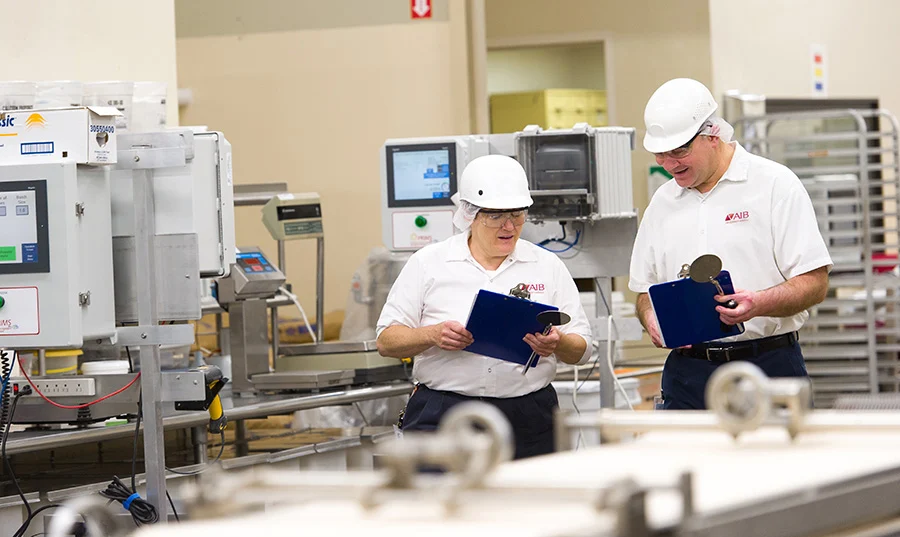

What Other Industries Benefit from Remote Temperature Monitoring Technology?
Remote temperature monitoring extends far beyond food service operations. The healthcare cold chain relies heavily on these systems to protect vaccines, blood products, and biological samples that require strict temperature control throughout storage and distribution.
Medical facilities use automated temperature monitoring to safeguard vaccine inventories worth thousands of dollars. A single temperature excursion can compromise entire batches of immunizations, creating both financial losses and public health risks. Hospital pharmacies, pathology labs, and blood banks deploy wireless sensors to track conditions in medical refrigerators and freezers around the clock.
How Does Pharmaceutical Storage Utilize This Technology?
Pharmaceutical storage facilities face stringent regulatory requirements that mirror food safety standards. Medications, insulin, and biologics demand precise temperature maintenance to preserve their efficacy and safety profiles.
Pharmaceutical wholesalers and retail pharmacies implement remote monitoring systems to:
- Track temperature-sensitive medications in storage areas
- Document compliance with Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) requirements
- Receive instant alerts when refrigeration units malfunction
- Generate audit-ready reports for regulatory inspections
Compounding pharmacies particularly benefit from continuous monitoring when preparing custom medications that require specific storage conditions. The automated documentation eliminates manual temperature logs while providing more reliable data capture.
What Role Does Supply Chain Monitoring Play?
Supply chain monitoring applications span multiple temperature-sensitive industries. Cold storage warehouses, refrigerated transport companies, and logistics providers use these systems to maintain product integrity during transit and storage.
Distribution centers handling perishable goods install sensors throughout their facilities to:
- Monitor different temperature zones simultaneously
- Track conditions in loading docks and staging areas
- Verify proper functioning of refrigerated trucks before dispatch
- Document chain of custody for high-value shipments
Research laboratories conducting clinical trials depend on remote monitoring to protect study samples and experimental materials. Universities and biotechnology companies use the technology to safeguard years of research work stored in ultra-low temperature freezers.
Why Does Technology Robustness Matter Across Industries?
The cross-industry adoption of remote temperature monitoring validates the technology’s reliability and versatility. Systems designed for food safety applications translate seamlessly to healthcare and pharmaceutical environments because the core requirements remain consistent: continuous monitoring, instant alerts, automated documentation, and regulatory compliance.
Embrace the Future of Food Safety with Remote Temperature Monitoring Systems!
Should your food business invest in remote temperature monitoring now? Yes—modern regulatory demands and operational realities make automated monitoring systems essential rather than optional for Australian food brands managing multiple locations.
The benefits remote temperature monitoring Australia delivers extend far beyond simple compliance. These systems transform how multi-location food brands efficiency operates, replacing error-prone manual processes with reliable, automated data collection that works around the clock.
Regulatory bodies increasingly expect digital records and continuous monitoring capabilities. Traditional paper-based logging systems cannot match the accuracy, consistency, and accessibility that Remote Temperature Monitoring Australia: How It Works for Multi-Location Food Brands demonstrates across diverse operational environments.
Key advantages driving adoption include:
- Immediate risk mitigation through instant alerts preventing costly spoilage incidents
- Simplified audit preparation with comprehensive digital records readily available
- Reduced labour costs by eliminating repetitive manual temperature checks
- Enhanced brand protection through consistent food safety standards across all sites
- Operational insights revealing energy inefficiencies and equipment performance issues
The technology has proven itself across demanding industries from pharmaceuticals to hospitality. Food brands delaying adoption face mounting compliance risks, higher operational costs, and competitive disadvantages. Battery-backed systems ensure reliability even during power failures, making these solutions robust enough for Australia’s diverse climate conditions and operational challenges.
Investing in remote temperature monitoring positions your brand to meet current regulations while preparing for increasingly stringent future requirements.
Click here for more Food Safety Temperature Monitoring: How to Prevent Spoilage and Equipment Failure
SERP Psychology: How SEO Agencies Manipulate User Intent to Win Every Keyword
Introduction: Why Most SEO Strategies Fail in 2025
In 2025, ranking on Google is no longer just about keywords or backlinks. Many SEO strategies fail because they ignore the psychological aspect of search behavior and user intent. Modern search engines, now dominated by AI-powered platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and Claude, prioritise content that anticipates user intent, satisfies queries, and aligns with engagement metrics.
SEO agencies that understand SERP psychology can manipulate how users interact with search results, ensuring their content captures clicks, dwell time, and conversions. This article dives into outdated SEO tactics, how AI is reshaping rankings, frameworks elite agencies use to fix failing strategies, actionable steps, and why integrating SERP psychology is now essential.
Why Most SEO Strategies Fail in 2025
1. Obsessing Over Keywords Instead of Intent
Businesses still target high-volume keywords without understanding why users search them. AI-driven search evaluates context and intent, making keyword-only strategies obsolete.
2. Neglecting Engagement Signals
Click-through rate (CTR), dwell time, scroll depth, and interaction metrics influence AI ranking models. Pages that fail to engage users drop in visibility regardless of keyword optimisation.
3. Thin or Unfocused Content
Generic content may attract initial indexing but fails to satisfy search intent. AI engines prioritise pages that offer comprehensive, structured, and actionable solutions.
4. Ignoring AI-Powered Search
Traditional SEO overlooks Answer Engine Optimisation (AEO). AI-driven search prefers direct answers, semantic relevance, and entity authority, meaning non-optimised pages get buried.
5. Poor Technical and UX Implementation
Slow pages, missing schema, and non-responsive design reduce both search engine understanding and user engagement, lowering performance even if content is good.
Outdated SEO Methods Businesses Still Use
Despite AI-first search and user-centric metrics, many marketers continue using methods that no longer deliver results:
- Keyword stuffing and meta over-optimisation – hurts readability and engagement.
- Generic blog posts – fail to capture attention or satisfy AI evaluation.
- Low-quality backlinking – no longer builds sustainable authority.
- Ignoring structured data – prevents snippet extraction.
- Neglecting behavioural signals – bounce rate, dwell time, and scroll depth influence rankings.
These outdated strategies explain why some websites look search-friendly but fail to win in SERPs.
AEO Insights: How AI & Answer Engines Are Changing Ranking
Answer Engine Optimisation ensures content aligns with AI and search engine interpretation, focusing on clarity, intent, and answerability.
Core Principles of AEO
- Answerability – Direct and precise answers outperform generic content.
- Semantic Depth – Cover all subtopics and related entities for full context.
- Entity Authority – Verified authors, brands, and references build trust.
- Zero-Click Optimisation – Featured snippets, People Also Ask, and knowledge panels dominate attention.
- Behavioural Signals – CTR, dwell time, and scroll depth are critical AI ranking factors.
Optimising for AEO ensures pages capture AI attention, user engagement, and conversions simultaneously.
Modern SEO Frameworks Elite Agencies Use
Top agencies integrate psychology, AI, and hybrid SEO frameworks to convert SERP clicks into meaningful engagement.
1. Technical SEO Foundation
Before manipulating SERPs, agencies ensure:
- Mobile-first and responsive design
- Fast-loading pages with optimised images
- Structured schema markup for AI snippet extraction
- Secure hosting with SSL certificates
Without technical optimisation, user intent cannot be captured effectively.
2. Semantic and Entity Mapping
Agencies map entities, topics, and semantic clusters to dominate SERPs:
- Identify transactional and informational queries
- Build content clusters for authority
- Internal linking reinforces hierarchy
- PR mentions increase topical credibility
Semantic mapping ensures AI engines extract and present answers correctly.
3. Psychological Copywriting & AI-Assisted Content
Money pages and content are crafted to trigger psychological responses:
- Headlines that evoke curiosity
- Storytelling that keeps users engaged
- AI-assisted semantic enrichment for zero-click visibility
- FAQ and structured answer blocks for featured snippets
This approach ensures users engage, click, and convert before ranking improves.

4. Behavioural Optimisation
Engagement metrics now dictate ranking:
- Optimise CTAs for visibility and action
- Use interactive elements to increase dwell time
- Reduce bounce with intuitive layouts
- Track scroll depth to identify content drop-off
Behavioural signals are crucial for AI-driven SERP positioning.
5. E-E-A-T Reinforcement
Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness remain essential:
- Verified author bios and professional experience
- Accurate references and citations
- Social proof, reviews, and testimonials
Strong E-E-A-T ensures SERP trust signals align with human and AI expectations.
6. AI-Friendly Answer Blocks
Content is structured to capture zero-click traffic:
- FAQs and Q&A sections for snippet extraction
- Short, actionable summaries
- Step-by-step guides for clarity
This increases both AI visibility and user conversion, even before high rankings.
Realistic Examples and Statistics
- Example 1: An e-commerce client applied SERP psychology and AI-assisted content to increase CTR by 52%, capturing top snippet positions without full rankings.
- Example 2: A SaaS company structured FAQs and entity-rich content, boosting zero-click leads by 47% in three months.
- Statistic: BrightEdge 2025 reports 70% of top-ranking pages incorporate behavioural and AI-aligned optimisation.
- Expert Insight: SEO strategist Kevin Morales states: “Understanding SERP psychology is no longer optional; it’s the difference between clicks and conversions.”
Actionable Steps to Apply SERP Psychology
- Conduct a Behavioural & UX Audit: Analyse CTR, dwell time, and scroll metrics.
- Map Semantic Clusters and User Intent: Align content with transactional and informational queries.
- Add AI-Friendly Answer Blocks: FAQs, summaries, and step-by-step guides.
- Strengthen E-E-A-T Signals: Verified authors, citations, testimonials, and reviews.
- Optimise CTAs & Interactive Elements: Ensure conversion-focused elements are visible and persuasive.
- Refine Headlines for Curiosity & Intent: Psychological triggers increase engagement.
- Test & Iterate: Use A/B testing to optimise CTR, dwell time, and conversions.
Conclusion: The SEO Reset Approach
In 2025, SEO success requires understanding SERP psychology, AI optimisation, and behavioural signals. Simply ranking is no longer enough—websites must anticipate intent, engage users, and convert traffic before algorithmic validation.
The SEO Reset approach combines technical excellence, semantic depth, AI-friendly content, and psychological persuasion. Businesses adopting this methodology win keywords, dominate featured snippets, maximise zero-click visibility, and convert traffic efficiently.
FAQs
1. What is SERP psychology in SEO?
SERP psychology is the study of how users behave in search results and how content can influence clicks, engagement, and conversions. Elite agencies use it to optimise headlines, summaries, FAQs, and CTAs, aligning content with human intent and AI evaluation for maximum visibility and performance.
2. Why do traditional SEO strategies fail today?
Traditional strategies focus on keywords, backlinks, and meta tags without considering user intent, AI optimisation, or behavioural engagement. Modern search engines prioritise semantic relevance, entity authority, and user interaction, rendering outdated methods ineffective for ranking, click-through, and conversions.
3. How does AEO impact SERP performance?
Answer Engine Optimisation ensures content is structured, answerable, and contextually relevant for AI-powered search. Pages optimised for AEO capture featured snippets, People Also Ask, and zero-click traffic, aligning user engagement and algorithmic understanding to maximise rankings and conversions.
4. What strategies do top agencies use to win keywords?
Top agencies integrate semantic mapping, AI-assisted content, behavioural optimisation, and psychological copywriting. They craft money pages and FAQs that anticipate intent, engage users, and convert traffic, ensuring pages perform in SERPs even before achieving full ranking positions.
5. How can businesses apply SERP psychology immediately?
Start by auditing behavioural metrics, mapping semantic topics, adding AI-friendly answer blocks, strengthening E-E-A-T signals, and refining headlines and CTAs. Continuous testing and iterative improvements ensure content aligns with user intent, maximises engagement, and wins keywords efficiently.
Why Restaurants Are Switching to Restaurant Food Safety Software
Why are restaurants abandoning clipboards and paper logs? The answer lies in the growing complexity of food safety compliance and the limitations of traditional manual tracking methods. For decades, restaurant managers relied on handwritten temperature logs, paper checklists, and filing cabinets full of documentation to meet health department requirements.
Restaurant food safety software represents a fundamental shift in how establishments protect customers and maintain regulatory standards. Digital platforms now handle everything from automated temperature monitoring to instant compliance reporting, eliminating the inefficiencies and human errors inherent in paper-based systems.
The digital transformation in restaurants extends beyond point-of-sale upgrades and online ordering. Food safety compliance has become a critical area where technology delivers measurable improvements in accuracy, efficiency, and risk prevention. Modern software solutions address the real-world challenges managers face daily: incomplete logs, missed temperature checks, lost documentation, and the constant pressure of surprise health inspections.
Why Are Restaurants Prioritizing Compliance with Food Safety Regulations?
Restaurants are required to follow strict rules set by various regulatory bodies, which makes compliance essential. Local health departments conduct surprise inspections, state agencies enforce specific handling requirements, and federal laws like FSMA (Food Safety Modernization Act) establish minimum standards for the industry. If restaurants fail to meet these requirements, they can face immediate closures, large fines, or damage to their reputation.
The Operational Challenges of Compliance
Staying compliant with food safety regulations can be complex and burdensome for restaurants. They have to manage multiple protocols and standards simultaneously:
- Tracking HACCP compliance protocols
- Maintaining SQF standards for quality assurance
- Documenting every critical control point in their food handling processes
Each regulation has its own specific record-keeping formats, temperature logs, sanitation schedules, and documentation for corrective actions.
The Risks of Manual Compliance Management
Relying on manual processes for compliance management introduces several risks:
- Staff may forget to complete required temperature checks during busy service periods
- Paper logs can be lost, damaged, or filled out incorrectly
- Training documentation becomes scattered across multiple binders and folders
- Audit preparation requires hours of sorting through handwritten records
The Consequences of Non-Compliance
The consequences of non-compliance go beyond just regulatory penalties. A single outbreak of foodborne illness linked to a restaurant can ruin years of brand building and customer trust. Violations lead to increased insurance premiums, and repeat offenders may face permanent closure.
These risks are driving restaurant operators to see food safety regulations as more than just bureaucratic obstacles. Instead, they view them as necessary frameworks that require systematic solutions powered by technology.
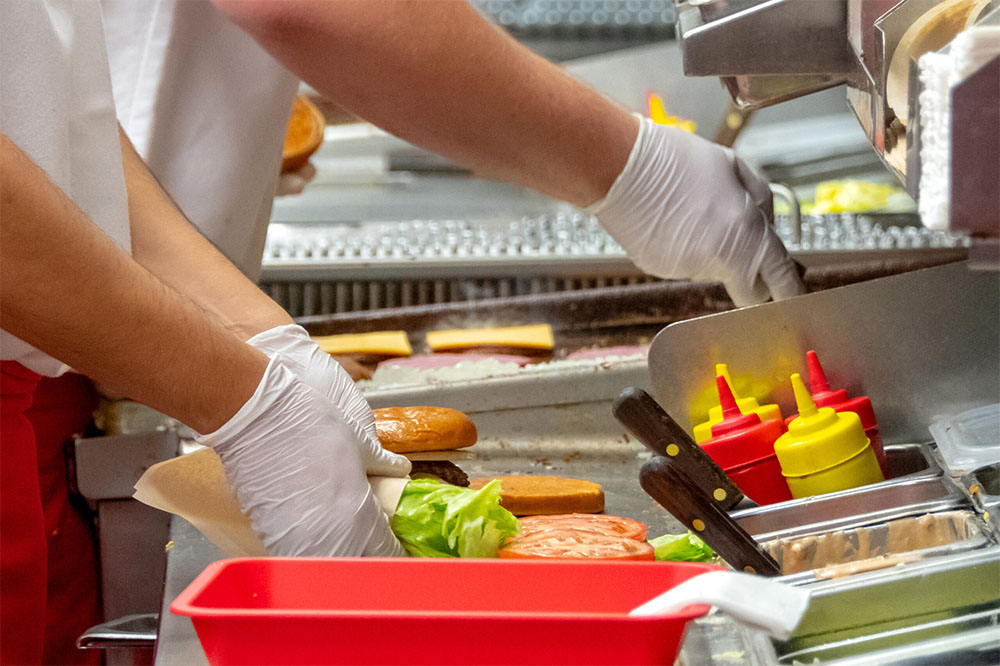

How Is Digital Transformation Changing Food Safety Practices?
Digital food safety logs are replacing traditional paper-based systems in restaurant kitchens nationwide. Centralized digital platforms eliminate the need for clipboards, binders, and manual record-keeping that often result in lost documentation or illegible entries.
The shift to digital systems addresses critical pain points in food safety management:
- Accuracy improvements come from eliminating human error in manual data entry. Temperature logging technology with wireless sensors automatically records refrigerator and freezer readings every few minutes, capturing data that staff might miss during busy service periods. Automated checklists guide employees through proper procedures step-by-step, reducing the risk of skipped tasks.
- Accessibility transforms operations by storing all food safety records in cloud-based systems. Managers can review compliance data from any location using smartphones or tablets. During health inspections, staff can instantly pull up weeks or months of documentation instead of searching through filing cabinets.
- Time-stamped digital records create an auditable trail that paper logs cannot match. Each entry includes the employee’s name, exact completion time, and any corrective actions taken. This level of detail proves invaluable during investigations or audits.
- Automated labeling systems generate expiration date stickers based on preparation times, ensuring FIFO (first-in, first-out) rotation. Staff simply scan or select items, and the system calculates proper use-by dates according to food safety guidelines.
What Are the Benefits of Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts?
Real-time temperature monitoring prevents food spoilage before it becomes a health hazard or financial loss. Wireless sensors installed in coolers, freezers, and hot-holding equipment continuously track temperatures and transmit data to centralized dashboards, eliminating the need for manual temperature checks every few hours.
When temperatures deviate from safe ranges, the system sends immediate alerts to managers and kitchen staff via text, email, or app notifications. A walk-in cooler experiencing a mechanical failure at 2 AM triggers an instant alert, allowing restaurants to address the problem before an entire inventory of perishables spoils. This proactive approach saves thousands of dollars in wasted food and protects customers from potential foodborne illness.
The technology also creates automatic documentation of temperature compliance. Every reading is timestamped and stored digitally, providing verifiable proof during health inspections that proper storage conditions were maintained. Staff no longer need to remember to record temperatures manually or risk incomplete logs that could result in violations.
This automatic documentation is also beneficial for food storage and distribution compliance, ensuring that all processes meet regulatory requirements.
Key advantages of spoilage prevention alerts include:
- Reduced food waste from undetected equipment failures
- 24/7 monitoring without additional labor costs
- Automatic compliance documentation for audits
- Quick response times that minimize inventory loss
This is why restaurants are switching to restaurant food safety software—the combination of continuous monitoring and instant notifications transforms food safety from a reactive process into a preventive system.
How Does Food Safety Software Improve Efficiency and Save Time?
Restaurant food safety software eliminates hours of manual labor by automating repetitive compliance tasks. Digital platforms handle daily checklist completion, temperature logging, and sanitation records without requiring staff to fill out paper forms, saving multi-unit franchises up to 2 hours per day per location.
Automation in restaurants transforms how teams prepare for health inspections. The software automatically compiles audit-ready documentation, organizing months of temperature logs, cleaning schedules, and corrective actions into accessible reports. Managers no longer spend hours searching through filing cabinets or deciphering handwritten notes before inspector visits.
Time-saving software features extend beyond basic record-keeping:
- Automated expiration date labeling generates and prints labels for prepped ingredients instantly
- Pre-scheduled task reminders notify staff when cleaning or equipment checks are due
- Digital signature capture eliminates the need to track down employees for sign-offs
- Bulk data entry allows one-click completion of routine checks across multiple stations
Staff productivity increases when employees spend less time on paperwork and more time on food preparation and customer service. Digital checklists guide workers through proper procedures step-by-step, reducing confusion and ensuring consistent execution. The software’s offline functionality means kitchen staff can complete tasks even during WiFi outages, with data syncing automatically once connectivity returns.
How Software Improves Team Accountability and Training
1. Better Management of Staff Training
Staff training management platforms change how restaurants keep track of employee food safety training. With digital systems, it’s easy to see who completed which training modules, when certifications expire, and which team members need refresher courses. Managers get automatic reminders before credentials expire, so there’s no chance of having untrained staff handling food.
2. Easy Access to Standardized Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Standardized operating procedures (SOPs) are now available to every team member through mobile-friendly interfaces. Instead of digging through binders or old printouts, employees can easily access step-by-step protocols for proper handwashing, temperature checks, or allergen handling on their tablets or smartphones. This quick access ensures that everyone follows the same procedures regardless of their shift or location.
3. Improved Communication and Accountability among the Workforce
Workforce communication tools integrated into food safety software promote accountability by being transparent. When a team member completes a temperature log or sanitation checklist, the system automatically records their action with a timestamp. Managers can spot patterns—like which employees often miss tasks or which shifts have more compliance issues—and provide targeted coaching to address these problems.
4. Empowering Staff to Report Issues and Ask Questions
Digital platforms also allow staff to report potential hazards or ask questions in real-time. For example, if a line cook notices unusual refrigerator temperatures, they can immediately flag the issue through the app, creating a documented record of corrective actions. This gives power to employees and makes food safety a shared responsibility among the entire team, where everyone understands their role in preventing contamination.
Why Is Enhanced Record-Keeping Important for Restaurants?
Why Restaurants Are Switching to Restaurant Food Safety Software becomes clear when examining record-keeping challenges. Digital audit logs eliminate the chaos of paper-based systems where documents get lost, damaged by kitchen spills, or become illegible over time.
Secure record keeping through cloud-based platforms protects critical compliance data from physical destruction. When health inspectors arrive unannounced, restaurants can instantly pull up months of temperature logs, cleaning schedules, and corrective action reports from any device. This health inspection readiness transforms what was once a stressful scramble through filing cabinets into a confident, streamlined process.
Paper logs create vulnerabilities that expose restaurants to serious risks:
- Incomplete entries where staff forget to sign off on tasks
- Falsified records filled out retroactively to appear compliant
- Missing documentation when pages are torn or misplaced
- Illegible handwriting that makes verification impossible
Digital audit logs timestamp every entry automatically, creating an unalterable trail of who completed which task and when. Automated reminders ensure staff complete required checks on schedule rather than rushing to fill gaps before inspections. The software flags missing data immediately, allowing managers to address compliance gaps in real-time rather than discovering problems during audits.
This systematic approach to documentation protects restaurants from regulatory fines while building a defensible record that demonstrates consistent adherence to food safety protocols.
How Do Software Solutions Adapt to Evolving Food Safety Regulations?
Food safety regulations change frequently as health authorities update standards based on emerging research and foodborne illness trends. Software platforms address this challenge through regulatory updates integration that automatically incorporates new requirements into existing workflows without manual intervention.
When agencies like the FDA modify HACCP guidelines or introduce new FSMA provisions, modern food safety systems push compliance template updates directly to restaurant operators. These updates refresh digital checklists, adjust temperature thresholds, and modify documentation requirements to match current legal standards. Restaurants using these platforms maintain compliance without dedicating staff hours to researching regulatory changes or redesigning paper forms.
Adaptive software features allow customization based on jurisdiction-specific requirements. A restaurant chain operating across multiple states can configure location-specific protocols that reflect varying local health codes while maintaining standardized corporate policies. The software automatically applies relevant regulations to each site based on geographic parameters.
Cloud-based systems enable developers to monitor regulatory landscapes continuously and deploy updates remotely. When new allergen labeling laws take effect or sanitation protocols change, restaurants receive notifications and updated templates through their existing interface. This proactive approach eliminates the risk of operating under outdated procedures that could result in violations during health inspections or audits.
Can Food Safety Software Integrate with Broader Restaurant Operations?
Modern integrated restaurant management software eliminates the need for multiple disconnected systems by combining food safety protocols with essential operational functions. These unified operations platforms handle temperature monitoring alongside inventory tracking, employee scheduling, and team communication within a single interface.
The Value of Inventory Management Integration
Inventory management integration proves particularly valuable when connected to food safety features. When temperature sensors detect a cooler malfunction, the system automatically flags affected inventory items and calculates potential losses. Staff receive immediate notifications about compromised products, preventing contaminated ingredients from reaching customers while simultaneously updating stock counts and triggering reorder alerts.
Creating Accountability through Scheduling Integration
The connection between scheduling and food safety creates accountability structures that traditional paper systems cannot match. Managers assign specific safety tasks—such as equipment sanitization or temperature checks—directly to scheduled employees through the platform. The software tracks completion rates by individual team member and shift, identifying training gaps or compliance issues before health inspections occur.
Ensuring Consistent Communication
Communication tools embedded in these platforms ensure safety protocols reach every team member instantly. When regulations change or new procedures roll out, managers push updates through the same system employees already use for daily checklists and temperature logs. This centralized approach reduces confusion and maintains consistency across multiple locations, making it especially beneficial for restaurant chains managing standardized safety protocols at scale.

What Are Some Popular Restaurant Food Safety Software Options?
Does the market offer diverse solutions for different restaurant sizes and needs? Yes, several specialized platforms cater to varying operational scales and compliance requirements, each bringing distinct strengths to food safety management.
- Operandio stands out for multi-unit operations, offering centralized oversight across multiple locations with robust reporting capabilities. The platform’s strength lies in standardizing procedures across franchise networks while maintaining location-specific customization.
- Jolt targets small restaurants and single-site operations with straightforward digital checklists and temperature monitoring. Its user-friendly interface requires minimal training, making it accessible for teams with varying technical skills.
- FoodDocs leverages AI-powered setup to generate customized HACCP plans and monitoring procedures in minutes rather than weeks. The system analyzes your menu and operations to automatically create relevant food safety documentation, dramatically reducing implementation time.
- SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor) provides extensive template libraries and mobile-first inspection tools. The platform excels at visual documentation through photo capture and supports offline functionality for kitchens with unreliable connectivity.
- Safefood 360, MaintainIQ, and FreshCheq round out the options with specialized features like advanced supplier management, equipment maintenance tracking, and automated expiration labeling. Each platform addresses specific pain points restaurants face when managing food safety compliance across daily operations.
Conclusion
Restaurant food safety software is changing the way foodservice operations keep people safe and follow regulations. This technology solves important problems by using automated monitoring, simplified documentation, and immediate alerts to stop food safety issues before they happen.
By using these digital solutions, restaurants can enjoy many benefits such as:
- Lower labor costs
- Better compliance with regulations
- Increased responsibility among team members
The money spent on this investment will be returned through fewer violations, less food waste, and smoother operations that allow staff to prioritize customer service instead of doing paperwork manually.
The real question is not whether you should use food safety software or not, but rather which solution is the best fit for your specific needs and size of your operation.
Click here: Why Smart Food Safety Temperature Monitoring Is Crucial for Restaurants
Why Smart Food Safety Temperature Monitoring Is Crucial for Restaurants
What is Smart Food Safety Temperature Monitoring and Why is it Important for Restaurants?
Smart food safety temperature monitoring uses digital sensors and automated systems to track and record food storage temperatures continuously, replacing or supplementing traditional manual checks with thermometers. These systems alert staff immediately when temperatures drift outside safe ranges, creating a proactive defense against food safety risks.
Restaurant food safety temperature monitoring depends heavily on maintaining precise temperature control throughout food storage, preparation, and service. Smart monitoring systems serve as the backbone of this critical operation, providing:
- Continuous surveillance of refrigeration units, freezers, and hot holding equipment
- Automated documentation that simplifies compliance record-keeping
- Instant notifications when equipment malfunctions or temperatures fluctuate
The importance of temperature control cannot be overstated in food service environments. A single refrigeration failure overnight can spoil thousands of dollars in inventory. More seriously, temperature abuse creates conditions where harmful bacteria multiply to dangerous levels within hours.
Poor temperature control leads to three devastating consequences: foodborne illness outbreaks that harm customers, regulatory violations resulting in fines or closures, and significant financial losses from spoiled inventory. Traditional manual monitoring—checking temperatures every few hours with handheld thermometers—leaves dangerous gaps where problems go undetected. Smart systems eliminate these blind spots, transforming temperature management from a periodic task into a constant safeguard.
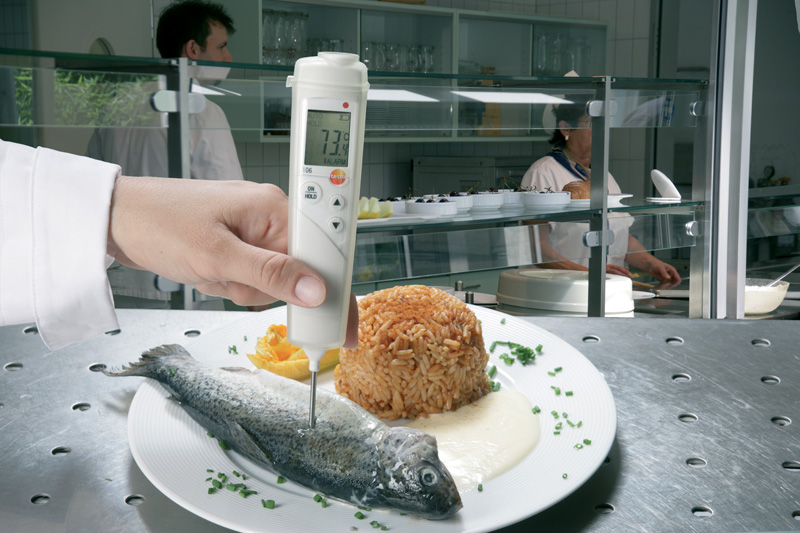

Why Must Restaurants Adhere to Food Safety Temperature Standards?
Restaurants must follow strict food safety standards because regulatory bodies worldwide recognize temperature control as the primary defense against foodborne illness. Health departments mandate specific temperature thresholds to create environments where harmful bacteria cannot thrive, protecting both customers and businesses from the devastating consequences of contaminated food.
Understanding Regulatory Temperature Requirements
Food safety regulations establish clear boundaries for safe food storage and service. Cold foods require refrigeration at 5°C or below, while hot foods must maintain temperatures of 60°C or above during holding periods. These numbers aren’t arbitrary—they represent scientifically validated thresholds where bacterial growth slows to negligible rates.
Refrigerated storage at or below 5°C creates conditions hostile to most pathogenic bacteria. At these temperatures, bacterial reproduction slows dramatically, extending the safe shelf life of perishable ingredients. The cold environment essentially puts bacteria into a dormant state, preventing the rapid multiplication that leads to food poisoning.
Hot holding requirements serve a different but equally critical purpose. Maintaining cooked foods at 60°C or higher doesn’t just slow bacterial growth—it actively destroys many harmful microorganisms. This temperature range ensures that foods prepared in advance remain safe for service throughout meal periods.
The Temperature Danger Zone Explained
The range between 5°C and 60°C represents what food safety experts call the temperature danger zone. Within this range, bacteria multiply at alarming rates, potentially doubling their population every 20 minutes under optimal conditions. A single bacterium can become millions within hours when food sits in this critical temperature band.
Common scenarios that push food into the danger zone include:
- Leaving ingredients on prep counters during extended preparation periods
- Inadequate cooling of large batches of cooked food
- Holding hot foods in warming equipment that doesn’t maintain proper temperatures
- Thawing frozen items at room temperature
- Storing food in overcrowded refrigerators with poor air circulation
The danger zone poses particular risks during food transitions—when items move from cooking to cooling, from storage to preparation, or from kitchen to service. Each of these moments creates opportunities for temperature abuse if staff don’t follow proper protocols.
To mitigate these risks, it’s essential for restaurant staff to adhere strictly to food safety prevention measures. Restaurant kitchens face unique challenges in avoiding the danger zone. High ambient temperatures from cooking equipment, frequent door openings, and large volumes of food being prepared all contribute to fluctuations in temperature that can compromise safety.
How Does Temperature Monitoring Prevent Foodborne Illness Outbreaks?
Temperature monitoring is the main way to prevent foodborne illness outbreaks. It does this by controlling the environment where harmful bacteria can grow. When restaurants don’t keep temperatures at the right levels, they create perfect conditions for pathogens to multiply and reach dangerous levels that can make customers sick within hours of eating.
Where Bacteria Hide in Restaurant Environments
Bacteria are present everywhere in food service operations, which means there is always a risk of contamination without proper controls in place. Here are some common places where bacteria can be found:
- Raw meats, poultry, and seafood: These items already contain natural bacteria such as Salmonella, Campylobacter, and E. coli when they arrive at restaurants.
- Fresh produce: Pathogens can be present on fresh fruits and vegetables due to contact with contaminated soil or irrigation water.
- Air circulation: The air in kitchens can carry bacterial spores that settle on food surfaces.
Food handlers also play a role in introducing bacteria into the environment. This can happen through direct contact with skin, respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing, and improper handwashing practices. Additionally, cutting boards, knives, and preparation surfaces can become breeding grounds for bacteria if they are not properly cleaned and sanitized between uses.
Water used for washing vegetables or making ice can also be a source of microorganisms if the sourcing or filtration systems are not functioning properly.
The kitchen environment has many opportunities for cross-contamination to occur:
- Refrigeration units: Raw and cooked foods should never share the same space in refrigeration units to prevent cross-contamination.
- Prep stations: Multiple ingredients being handled simultaneously at prep stations can lead to bacterial transfer if proper hygiene practices are not followed.
- Serving areas: Food that sits exposed to ambient temperatures in serving areas is at risk of bacterial growth.
- Storage zones: Temperature fluctuations in storage areas can go unnoticed and create conditions for bacterial multiplication.
The Speed of Bacterial Reproduction Under Poor Temperature Control
Bacteria reproduce by splitting into two, doubling their population every 20 minutes when conditions are ideal. If food is left in the danger zone (between 40°F and 140°F) for too long, a single bacterium can turn into over one million cells in just seven hours. This rapid growth turns a small contamination problem into a serious health threat.
One specific bacterium of concern is Staphylococcus aureus, which produces toxins that cause illness even after the bacteria itself is killed by cooking. If contaminated food stays at room temperature for just four hours, enough toxin can build up to cause vomiting and diarrhea in healthy adults. Children, elderly patrons, and individuals with weakened immune systems face even greater risks from smaller amounts of bacteria.
Temperature abuse scenarios happen more often than many restaurant operators realize:
- Morning prep work left on counters while staff handle other tasks
- Buffet setups where food sits out for extended periods without temperature control
- Delivery delays causing perishable items to remain outside safe temperature ranges
- Cooling processes that take too long or are improperly executed
By implementing effective temperature monitoring practices, these potential risks can be mitigated.
What Are the Compliance Requirements for Temperature Monitoring in Restaurants?
Restaurants must meet specific regulatory compliance standards for temperature monitoring equipment and procedures. Health departments mandate that all thermometers used for food safety checks maintain an accuracy of ±1°C (or ±2°F), ensuring readings are precise enough to detect when food enters the danger zone. This strict accuracy requirement exists because even a small temperature deviation can mean the difference between safe food and rapid bacterial multiplication.
Mandatory Temperature Check Protocols
Health code adherence requires restaurants to implement systematic temperature monitoring schedules. Food service establishments must check and record temperatures of refrigerated foods, frozen items, and hot-held dishes at regular intervals throughout each operating day. The standard requirement calls for temperature checks every 2-4 hours during service periods, though high-risk establishments may face more frequent monitoring mandates.
Documentation forms the backbone of regulatory compliance. Restaurants must maintain detailed temperature logs that include:
- Date and time of each temperature check
- Specific food item or storage unit tested
- Recorded temperature reading
- Name or initials of staff member conducting the check
- Corrective actions taken if temperatures fall outside safe ranges
These records must typically be retained for a minimum of 30-90 days, depending on local health department requirements. Inspectors routinely review these logs to verify consistent monitoring practices.
Temperature Monitoring Methods Recognized by Health Authorities
Regulatory bodies accept various temperature checking methods, provided they meet accuracy standards. Manual probe thermometers remain the most common tool, requiring staff to insert the probe into the geometric center of food items to obtain accurate core temperatures. The thermometer must penetrate at least 5 cm into larger food items to ensure the reading reflects the coldest or hottest internal point.
Infrared thermometers offer non-contact surface temperature readings but face limitations in regulatory acceptance. Health codes typically require infrared devices only for surface checks of packaging or equipment
Why Is Consistent Temperature Monitoring Critical in Daily Operations?
Consistent temperature monitoring is essential for daily food safety operations because temperatures can change at any time during service hours. For example, a refrigeration unit might break down during a busy lunch rush, or a hot holding station could drop below safe temperatures without anyone noticing. If there are no regular checks in place, these dangerous situations can go undetected, putting customers at risk and exposing the restaurant to legal issues.
How Often Should Restaurants Check Food Temperatures?
Food safety authorities recommend checking temperatures every 2-4 hours for all potentially hazardous foods in storage, display, and holding areas. This frequency strikes a balance between maintaining safety and allowing staff to focus on other operational duties. High-risk establishments or those serving vulnerable populations may need more frequent checks, sometimes hourly during peak service times.
The 2-4 hour window exists because bacterial growth speeds up quickly once food enters the danger zone. Within this timeframe, restaurants can identify problems and take corrective action before bacterial levels become dangerous. Waiting longer between checks creates gaps where contamination can develop without being noticed.
What Tools Enable Consistent Temperature Checks?
Probe thermometers are still the most common manual tool used to verify temperatures. These handheld devices allow staff to quickly check the internal temperatures of food by inserting the probe into the thickest part of the product. It’s important for staff to sanitize probes between uses to prevent cross-contamination and calibrate them regularly to maintain accuracy.
Manual checking with probe thermometers requires discipline and documentation. Staff must:
- Record each temperature reading along with the time and location
- Initial the log to confirm who performed the check
- Note any corrective actions taken for temperatures that are out of range
- Store logs for regulatory inspection purposes
Digital temperature systems represent a significant advancement in continuous monitoring capabilities. These automated solutions use wireless sensors placed in refrigerators, freezers, hot holding units, and preparation areas. The sensors transmit real-time temperature data to a central monitoring platform accessible via computer or mobile device.
Smart digital systems eliminate the potential for human error that comes with manual checks. Sensors never forget to take readings, never misread displays, and never fail to document results. They provide uninterrupted surveillance 24 hours per day, including overnight hours when staff may not be present.
It’s crucial to remember that proper storage is also an essential part of maintaining food safety standards. Regularly consulting resources like this study guide from ServSafe can provide valuable insights into best practices for food safety and temperature monitoring.
How Smart Temperature Monitoring Systems Help Reduce Waste and Increase Profits
Smart temperature monitoring systems directly reduce food waste by identifying temperature changes before products spoil. When refrigeration units break down or hot holding equipment fails to maintain proper temperatures, food quality deteriorates rapidly, forcing restaurants to throw away entire batches of ingredients or prepared meals.
The Hidden Cost of Manual Temperature Checks
Manual temperature monitoring creates gaps in oversight that lead to significant financial losses. A restaurant checking temperatures every four hours leaves substantial windows where equipment failures go undetected. During these gaps, a malfunctioning walk-in cooler can bring temperatures into the danger zone, compromising hundreds of dollars worth of fresh produce, dairy products, and proteins.
The financial impact extends beyond the immediate cost of discarded food. Restaurants must account for:
- Labor costs associated with preparing replacement items
- Emergency ingredient purchases at premium prices
- Lost revenue from menu items temporarily unavailable
- Staff time spent documenting and disposing of spoiled products
Automated Alerts Transform Spoilage Prevention
Smart monitoring systems eliminate detection delays through continuous temperature surveillance. These systems send instant notifications when temperatures deviate from safe ranges, allowing managers to respond within minutes rather than hours. A refrigeration unit beginning to fail at 2 AM triggers an alert, enabling staff to transfer products to backup storage before spoilage occurs.
The speed of response makes the difference between saving inventory and accepting losses. Traditional manual checks might not discover the malfunction until the morning shift arrives, by which point perishable items have spent hours in unsafe temperatures. Automated systems compress response times from hours to minutes, preserving product integrity and protecting profit margins.
Data-Driven Inventory Management
Temperature monitoring systems generate detailed records that reveal patterns in equipment performance and product storage. These analytics help restaurants optimize inventory ordering by identifying which storage units maintain the most consistent temperatures for specific product types. A restaurant might discover that certain refrigeration zones experience more temperature variability, prompting them to store less sensitive items in those areas.
Historical temperature data supports more accurate inventory forecasting. Restaurants can analyze how temperature consistency affects product shelf life, allowing them to adjust ordering quantities and frequencies. Products stored in equipment with stable temperature control last longer, reducing the need for frequent reordering and minimizing emergency purchases.
Quantifying the Financial Return
What Role Does Staff Training Play in Effective Temperature Control?
Staff training is essential for any successful temperature monitoring program. Even the most advanced smart monitoring systems cannot work effectively without employees who know how to use them correctly. Training ensures that every team member—from kitchen staff to managers—knows how to operate thermometers, interpret readings, and respond appropriately when temperatures fall outside safe ranges.
Why Is Proper Equipment Usage Education Non-Negotiable?
Restaurant staff must receive comprehensive instruction on thermometer calibration, probe placement, and reading interpretation. A probe thermometer inserted incorrectly into food can provide false readings, creating a dangerous illusion of safety. Staff need to understand that checking the thickest part of meat, avoiding contact with bones, and waiting for temperature stabilization are critical steps that directly impact food safety outcomes.
Digital monitoring systems require specific operational knowledge. Employees should learn how to:
- Verify sensor accuracy through regular calibration checks
- Position wireless sensors correctly in refrigeration units and hot holding equipment
- Interpret dashboard readings and recognize when alerts require immediate action
- Document temperature logs accurately for compliance records
- Troubleshoot common issues such as sensor disconnections or battery warnings
Training sessions should include hands-on practice with actual equipment used in the establishment. This practical experience builds confidence and reduces the likelihood of errors during busy service periods.
How Does Training Support Adherence to Safety Standards?
Understanding the “why” behind temperature protocols transforms compliance from a checkbox exercise into a meaningful practice. When staff members grasp that the 5°C to 60°C danger zone allows bacteria to double every 20 minutes, they recognize the urgency of maintaining proper temperatures. This knowledge creates internal motivation that extends beyond fear of disciplinary action.
Trained employees become active participants in the food safety culture rather than passive rule-followers. They develop the ability to identify potential risks before they escalate into violations. A line cook who understands temperature danger zones will notice when a refrigerator door has been left ajar and take immediate corrective action without waiting for a supervisor’s instruction.
Regular refresher training reinforces proper protocols and updates staff on new equipment or revised procedures. These sessions provide opportunities to address common mistakes, share best practices, and discuss real scenarios encountered in the restaurant. Role-playing exercises where staff
How Can Smart Monitoring Enhance Overall Food Safety Protocols?
Smart monitoring transforms temperature tracking from an isolated task into a cornerstone of comprehensive food safety management. These systems create a foundation that connects with every aspect of restaurant operations, from cleaning schedules to crisis response procedures, establishing a unified approach to protecting food quality and customer health.
Creating Synergy Between Temperature Control and Sanitation
Temperature monitoring gains exponential value when paired with hygiene standards integration. Smart systems document not just temperature readings but create a complete timeline of food safety activities throughout the day. When staff log refrigerator temperatures, the same platform can prompt them to verify cleaning tasks, check sanitizer concentrations, and confirm handwashing protocols have been followed.
This interconnected approach reveals patterns that single-focus monitoring misses. A restaurant might discover that temperature fluctuations in a walk-in cooler coincide with periods of heavy traffic and frequent door openings. The same data shows whether staff are maintaining proper hand hygiene during these busy periods. Integrated safety protocols eliminate blind spots by treating food safety as a holistic system rather than separate checklists.
Digital platforms allow managers to set up automated workflows that link related safety tasks. When a staff member records the temperature of a prep station, the system can automatically trigger reminders for surface sanitization or equipment cleaning. This creates natural connections between temperature control and cleanliness standards, ensuring nothing falls through the cracks during rush periods.
Strengthening Audit Readiness and Documentation
Smart monitoring systems serve as continuous preparation for health inspections and internal audits. Traditional paper logs often contain gaps, illegible entries, or retrospective fill-ins that raise red flags during inspections. Digital systems timestamp every entry and prevent data manipulation, creating an audit trail that demonstrates genuine compliance.
Health inspectors increasingly value electronic records that show consistent monitoring patterns. These systems can instantly generate reports covering any time period, displaying temperature trends, staff compliance rates, and corrective actions taken. When an inspector asks about refrigeration practices from three months ago, managers can pull up detailed records within seconds rather than searching through stacks of paper.
The documentation extends beyond routine monitoring. Smart systems record:
- Exact times when temperature deviations occurred
- Duration of any excursions outside safe ranges
- Staff members who responded to alerts
- Corrective measures implemented
Additionally, smart monitoring plays a crucial role in food safety supplier management. By ensuring suppliers adhere to strict temperature control and hygiene standards through real-time monitoring and data analysis, restaurants can mitigate risks associated with foodborne illnesses and maintain high levels of customer satisfaction.
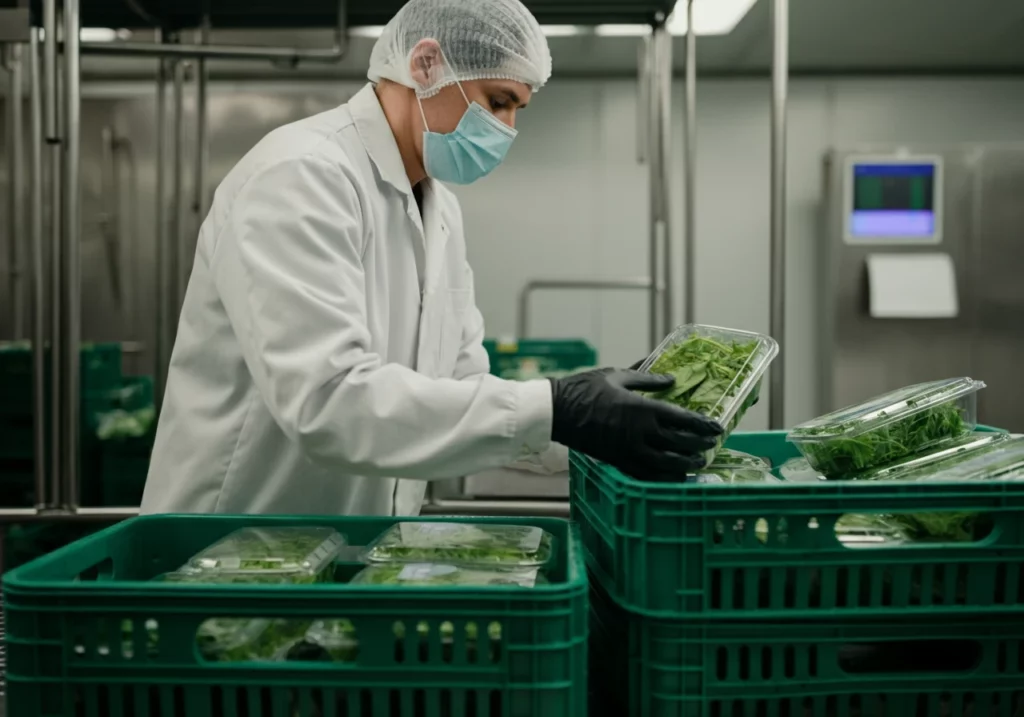

What Are the Benefits of Real-Time Alerts and Data Analytics in Smart Systems?
Real-time alerts transform temperature monitoring from a reactive task into a proactive safety measure. Smart systems instantly notify managers and staff when temperatures deviate from safe ranges, eliminating the risk of delayed responses that could compromise food safety. These alerts arrive via mobile notifications, email, or dashboard warnings, ensuring the right people receive critical information regardless of their location in the restaurant.
The immediate notification system addresses temperature fluctuations within minutes rather than hours. When a refrigeration unit begins warming beyond 5°C, alerts trigger before food enters the danger zone. This rapid response capability prevents scenarios where spoilage goes undetected until the next scheduled manual check, potentially saving entire inventory sections from disposal.
How Do Temperature Deviation Alerts Function in Practice?
Smart sensors continuously measure storage unit temperatures at intervals as frequent as every 30 seconds. The system compares these readings against preset parameters specific to each storage area. Walk-in coolers, reach-in refrigerators, and hot holding cabinets each maintain different thresholds tailored to their intended use.
When readings exceed acceptable ranges, the system initiates a tiered alert protocol:
- Level 1 alerts notify floor staff of minor deviations requiring immediate attention
- Level 2 alerts escalate to kitchen managers when temperatures remain outside safe zones for extended periods
- Level 3 alerts reach senior management and maintenance teams for equipment failures requiring urgent repair
This graduated response ensures appropriate personnel handle each situation based on severity. A door left ajar receives quick floor-level correction, while compressor failures immediately involve maintenance contractors.
What Role Does Continuous Supervision Technology Play?
Continuous supervision technology eliminates gaps in monitoring coverage that manual systems cannot avoid. Traditional probe thermometer checks occur every 2-4 hours, creating blind spots where temperature excursions remain undetected. Such manual temperature logs are no longer enough for food safety, as smart systems maintain constant vigilance, capturing every temperature fluctuation throughout 24-hour operations.
This uninterrupted monitoring proves particularly valuable during overnight hours when staffing levels decrease. Equipment malfunctions occurring at 3 AM receive the same immediate attention as daytime incidents. The system never sleeps, takes breaks, or forgets scheduled checks.
The technology also removes human error from the equation. Staff
Conclusion
Why Smart Food Safety Temperature Monitoring Is Crucial for Restaurants becomes clear when examining its multifaceted impact on modern food service operations. Smart temperature monitoring systems serve as the backbone of public health protection, preventing bacterial growth that leads to foodborne illness outbreaks. These systems simultaneously drive operational efficiency by automating what was once a labor-intensive manual process, freeing staff to focus on customer service and food preparation.
The financial benefits extend beyond labor savings. Restaurants implementing smart monitoring reduce food waste significantly by catching temperature deviations before products spoil. This protection of inventory directly improves profit margins while demonstrating environmental responsibility through reduced waste.
Customer trust in restaurants hinges on consistent food safety practices. Smart monitoring systems provide the documentation and reliability that customers expect, protecting brand reputation in an era where a single food safety incident can spread rapidly through social media and review platforms.
The technology landscape continues evolving, making smart temperature monitoring more accessible and affordable for restaurants of all sizes. Investing in these systems represents a commitment to:
- Protecting customer health through consistent temperature control
- Meeting regulatory requirements with automated documentation
- Reducing operational costs through waste prevention
- Building lasting customer loyalty through demonstrated safety standards
Restaurant operators who embrace smart temperature monitoring position their businesses for sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive and safety-conscious market.
Click here: Why Restaurants Are Switching to Restaurant Food Safety Software
How SEO Services Help Improve Google Rankings Faster
Introduction
Every business wants to rank higher on Google. After all, when your website appears on the first page of search results, you instantly gain more visibility, credibility, and customers. But here’s the truth—improving rankings isn’t just about sprinkling keywords into your website. It takes strategy, technical know-how, and consistent effort.
That’s where SEO services come in. In simple terms, SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the process of optimizing your website so search engines can easily understand it and rank it higher. SEO services take this one step further by using proven strategies to accelerate your visibility on Google, helping your business rise above competitors faster than if you tried doing it alone.
Let’s break down what SEO services are, why they matter, and how they can help your business achieve higher rankings more quickly.
What Are SEO Services?
SEO services are professional strategies designed to improve your website’s search performance. These services combine technical expertise, content optimization, and authority-building tactics to ensure your site not only ranks well but also attracts the right audience.
See more: Why Food Safety Traceability Software Matters in 2025
Common SEO services include:
- Keyword research – Identifying the search terms your target customers are using.
- On-page SEO – Optimizing content, meta descriptions, and internal linking.
- Technical SEO – Enhancing site speed, crawlability, and mobile performance.
- Off-page SEO – Building authority through backlinks and mentions.
- Local SEO – Targeting geographic searches like “plumber near me” or “best dentist in Chicago.”
- Content marketing – Publishing blogs, guides, and videos optimized for search.
When done right, these services create a strong foundation that allows your website to climb Google rankings faster.
Why SEO Matters for Businesses Today
In today’s competitive digital marketplace, ranking high on Google is no longer optional—it’s essential.
Here’s why SEO matters:
- Most journeys begin with search: Nearly all buying decisions start with a Google query.
- Organic clicks beat ads: Users often trust organic results more than paid ads.
- Mobile-first behavior: With most searches happening on smartphones, SEO ensures your site is optimized for mobile.
- Competitor advantage: If your competitors are investing in SEO and you’re not, they’re capturing the leads you’re missing.
- Algorithm updates: Google constantly changes its ranking system, and SEO ensures your site keeps up.
Without SEO, your website risks being invisible—even if you have the best products or services.
Key Benefits of SEO Services
Investing in SEO services offers more than just rankings. It creates measurable, long-term value for your business.
1. Increased Traffic
SEO ensures your site gets in front of the right audience, driving more qualified visitors.
2. Faster Results
With expert strategies, SEO services can help your site climb rankings more quickly than trial-and-error efforts.
3. Better Lead Quality
SEO targets intent-based searches, meaning the people who find your site are already interested in your services.

4. Higher Credibility
Websites on the first page of Google are perceived as more trustworthy.
5. Strong ROI
Unlike paid ads that stop when the budget ends, SEO continues to deliver long-term results.
6. Improved User Experience
SEO services focus on site speed, structure, and navigation—factors that keep users engaged.
Types of SEO Services
Understanding the different types of SEO helps clarify how each contributes to faster rankings.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO focuses on optimizing the visible elements of your website:
- Using keywords naturally in titles, headers, and content.
- Structuring content for readability and engagement.
- Internal linking to guide visitors to related pages.
Example: A bakery could optimize its menu page with phrases like “best cupcakes in Seattle” to rank for local searches.
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO builds your site’s authority through external signals:
- High-quality backlinks from trusted sites.
- Social shares and mentions.
- Listings in local directories.
Example: A law firm earns backlinks from reputable legal blogs, boosting credibility and ranking speed.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO ensures Google can crawl and index your site efficiently:
- Optimizing site speed.
- Ensuring mobile-friendliness.
- Fixing broken links and duplicate content.
- Implementing structured data for rich snippets.
Example: An e-commerce store improves page speed, reducing bounce rates and increasing rankings.
Local SEO
For businesses targeting specific regions, local SEO is crucial:
- Optimizing your Google Business Profile.
- Earning reviews from local customers.
- Adding city-based keywords to service pages.
Example: A dentist in Dallas ranks higher for “family dentist near me” by optimizing local SEO.
Content SEO
Content SEO ensures your website has fresh, relevant, and optimized material:
- Blog posts answering customer questions.
- Informational guides and how-to articles.
- Engaging videos and infographics.
Example: A fitness coach creates blog posts like “10-Minute Workouts for Busy Professionals” to rank quickly for niche queries.
How SEO Services Drive Business Growth Online
SEO isn’t just about faster rankings—it’s about sustainable growth.
- Attracts More Clients: Optimized websites rank for terms your audience is actively searching.
- Improves Conversions: Clear calls-to-action and user-friendly design turn visitors into customers.
- Saves Time: Experts know the right strategies to use, cutting down trial-and-error delays.
- Builds Long-Term Authority: Once established, strong rankings are easier to maintain.
Example: A small e-commerce store invests in SEO services. Within six months, their site ranks on the first page for “eco-friendly home products.” Traffic increases, sales rise, and they start competing with much larger brands.
Tips for Choosing the Right SEO Service Provider
Not every SEO provider is equal. Choosing wisely can determine how fast your rankings improve.
- Look for Experience: Providers with industry-specific knowledge deliver better results.
- Ask for Case Studies: Proven results show they know how to achieve rankings.
- Demand Transparency: A trustworthy provider explains strategies and shares reports.
- Customized Strategies: Avoid one-size-fits-all packages; your business needs tailored SEO.
- Realistic Expectations: Be wary of anyone promising #1 rankings overnight—SEO takes time.
- Focus on Both On-Page & Off-Page: A balance of both is key to long-term success.
Relatable Scenario
Imagine you’re a local roofing company. You rely on referrals, but new leads are slow. You invest in SEO services:
- Your website is optimized for “roof repair in Austin.”
- Local SEO puts your firm in Google’s map pack for “roofing near me.”
- Blogs about “Signs You Need a New Roof” start ranking quickly.
- Backlinks from home improvement sites strengthen authority.
Within months, calls for quotes double. Instead of waiting for word-of-mouth, your business is now visible to anyone searching online.
Conclusion
Ranking high on Google doesn’t happen overnight, but SEO services can speed up the process by applying proven strategies, technical expertise, and tailored solutions.
From on-page and off-page tactics to local and technical improvements, SEO is the foundation of digital visibility. More importantly, it ensures that when people search for businesses like yours, they find you—not your competitors.
Think of SEO not as an expense but as an investment. With the right SEO partner, your website can climb Google rankings faster, attract more qualified leads, and build long-term business success.
The sooner you start, the sooner your business will enjoy the benefits of higher rankings and sustainable growth.
Beginner’s Guide to SEO Optimalisatie: What You Need to Know
If you’re just getting started with SEO (Search Engine Optimization) in 2025, you’re in the right place. SEO optimalisatie is crucial for driving organic traffic to your website and ensuring it ranks high on search engine results pages (SERPs). However, with algorithms constantly evolving and new trends emerging, it can be overwhelming for beginners. This guide will walk you through the fundamental strategies that are still effective in 2025, including on-page and off-page SEO techniques. Whether you’re a business owner, blogger, or aspiring SEO professional, understanding these concepts is key to achieving long-term success online.
In this article, we’ll explore content optimization, backlink building, improving user experience (UX), mobile-first indexing, and EEAT (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) — the SEO strategies that matter in 2025. Plus, we’ll touch on outdated techniques that no longer work, helping you avoid common SEO mistakes.
1. What Is SEO Optimalisatie and Why Does It Matter?
SEO optimalisatie is the process of optimizing your website so that it ranks higher in search engine results, driving organic traffic to your site. Essentially, SEO involves both technical and creative elements aimed at improving your website’s visibility on search engines like Google.
Why does SEO matter? Well, the vast majority of online experiences start with a search engine. So, if your website isn’t visible in the search results, you’re missing out on potential traffic, leads, and sales. SEO is your ticket to attracting the right audience at the right time.
SEO Basics
SEO can be broken down into two main categories: on-page SEO and off-page SEO. On-page SEO refers to anything you do on your website to improve its ranking, while off-page SEO focuses on strategies that happen outside your website to build authority and trust.
2. On-Page SEO: Getting Your Website Ready for Search Engines
On-page SEO is about optimizing elements within your website to make it more search-engine friendly. This includes everything from the content you create to the way your site is structured. In 2025, on-page SEO is more important than ever, especially as Google’s algorithms become smarter and more user-focused.
Content Optimization: Quality Over Quantity
Content is still king in SEO. However, today’s SEO isn’t just about keyword stuffing. Google’s algorithms focus more on the context and quality of content rather than the sheer number of times a keyword appears.
Tip: Create content that answers your audience’s questions, provides valuable insights, and is engaging. Aim for long-form, high-quality content that satisfies search intent and addresses the needs of your target audience.
Best Practices:
- Use related keywords and semantic variations.
- Focus on answering user queries and providing useful information.
- Ensure your content is easy to read, well-structured, and engaging.
Meta Tags and Headings
Meta tags (including title tags and meta descriptions) play a key role in on-page optimization. These elements help search engines understand the content of your page and encourage users to click through to your website.
Tip: Use clear, concise, and engaging title tags that include relevant keywords. Write compelling meta descriptions that encourage clicks while accurately describing the content.
3. Off-Page SEO: Building Your Website’s Authority
Off-page SEO is equally important in boosting your rankings. This refers to activities you do outside of your website, such as acquiring backlinks and building brand authority. Backlinks, in particular, are one of the most important ranking factors for Google.
Backlink Building: Focus on Quality, Not Quantity
Gone are the days of buying hundreds of low-quality backlinks. In 2025, search engines like Google care more about the quality of the links pointing to your website than the number of links you have.
Tip: Focus on earning high-quality backlinks from authoritative sites in your industry. Guest blogging, content partnerships, and influencer outreach are great ways to earn valuable backlinks.
Best Practices:
- Reach out to industry influencers for collaborations.
- Create content that naturally attracts backlinks (e.g., in-depth guides, research studies, etc.).
4. User Experience (UX): A Crucial Ranking Factor
Google’s Core Web Vitals and user experience metrics are becoming increasingly important for SEO rankings in 2025. The better the user experience, the more likely your site is to rank well.

Speed and Mobile Responsiveness
Page speed and mobile responsiveness are critical ranking factors. A slow website or a site that doesn’t work well on mobile devices will result in higher bounce rates, which negatively impacts your SEO.
Tip: Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to test your site’s performance and make necessary improvements. Ensure your site is fully responsive and provides a seamless experience on both mobile and desktop.
Easy Navigation and Design
A well-designed website with easy-to-use navigation will keep visitors engaged and reduce bounce rates. A good UX encourages users to explore more pages on your site, increasing the chances of conversions and improving your SEO.
Tip: Simplify your website’s navigation, use clear calls to action, and ensure a clean, organized layout.
5. EEAT: Establishing Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness
EEAT (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) is becoming increasingly important for SEO, especially for websites in sensitive fields like health, finance, and law. Google rewards content that demonstrates expertise and trustworthiness.
Building Trust with Quality Content
To rank well, your website needs to be seen as an authority in your field. Google looks for websites that provide reliable, high-quality information.
Tip: Include author bios that highlight your qualifications and expertise, cite reputable sources, and regularly update your content to keep it accurate and relevant.
6. Outdated SEO Techniques to Avoid in 2025
As SEO evolves, certain techniques that worked in the past are now outdated and ineffective. Knowing which strategies to avoid can save you time and help you focus on what really works.
Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing was once a common practice, but it’s now a sure way to get penalized. Google’s algorithms now prioritize natural, helpful content rather than keyword-heavy content.
Tip: Avoid overusing keywords in your content. Focus on writing naturally while incorporating relevant keywords in a way that flows well.
Low-Quality Link Building
Buying backlinks or participating in link farms was once a common practice, but today, this can harm your site’s reputation and rankings.
Tip: Focus on earning natural, high-quality backlinks from reputable sources rather than resorting to questionable tactics.
7. Summary & Actionable Checklist
To effectively optimize your website and boost your traffic in 2025, follow this actionable checklist:
- Content Optimization: Focus on answering user intent and creating valuable, high-quality content.
- Backlink Building: Build high-quality, relevant backlinks from authoritative websites.
- Mobile Optimization: Ensure your website is mobile-friendly and fast-loading.
- Improve User Experience: Focus on speed, navigation, and design to enhance user experience.
- EEAT: Demonstrate your expertise and authority in your field to build trust with users and search engines.
- Avoid Outdated Tactics: Steer clear of keyword stuffing and low-quality link-building practices.
By following these strategies, you’ll be on your way to improving your website’s search rankings and driving more organic traffic.
Meta Description (150-160 words):
Learn the fundamentals of SEO optimalisatie in this beginner’s guide for 2025. Discover effective strategies like content optimization, backlink building, mobile-first indexing, improving user experience (UX), and focusing on EEAT (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness). Avoid outdated practices like keyword stuffing and low-quality link building. Whether you’re a marketer, blogger, or SEO professional, this guide provides actionable tips to help you boost your website’s rankings and drive more organic traffic.
releated:Content Consistency Practice is Key to Your SEO Success






